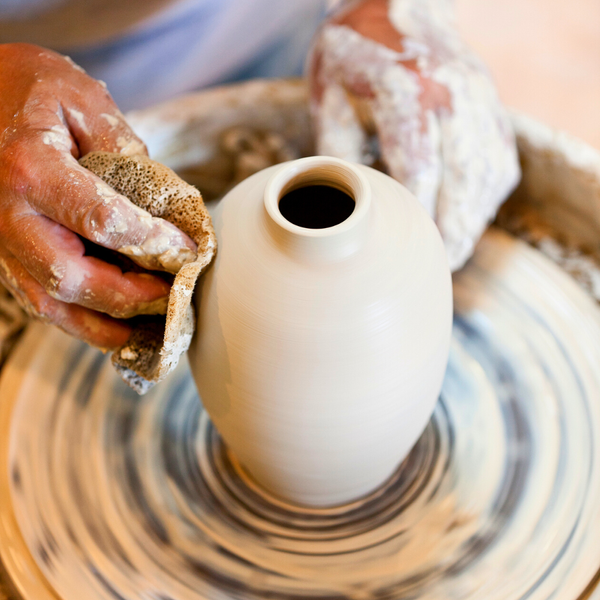
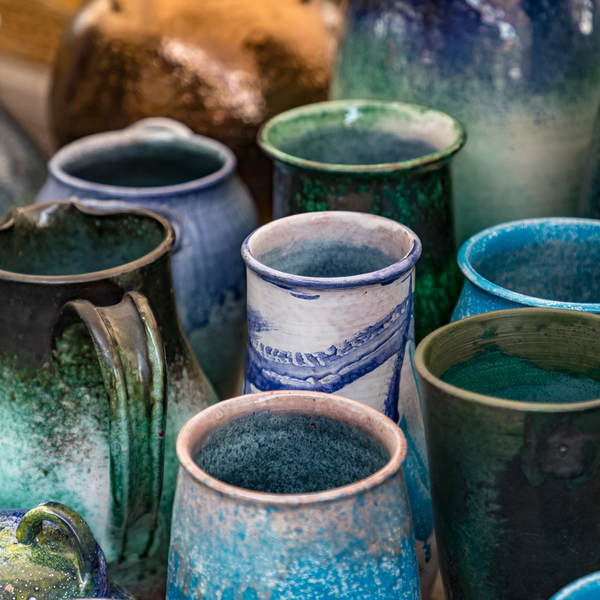
Pottery, an ancient craft that has stood the test of time, continues to captivate and inspire.
From the earliest human civilizations to modern-day artisans, the art of shaping and firing clay has evolved into a sophisticated practice.
In this journey through the world of pottery, we’ll uncover the unique characteristics and uses of the four primary types: Earthenware, Stoneware, Porcelain, and Bone China.
Get ready to explore their distinct properties, firing processes, and applications, and discover why these timeless forms of pottery remain beloved by artists and collectors alike.
Key Takeaways:
- Pottery is categorized into four main types: Earthenware, Stoneware, Porcelain, and Bone China.
- Each type of pottery has unique characteristics, firing temperatures, and uses.
- Understanding the properties of different clays is essential for successful pottery making.
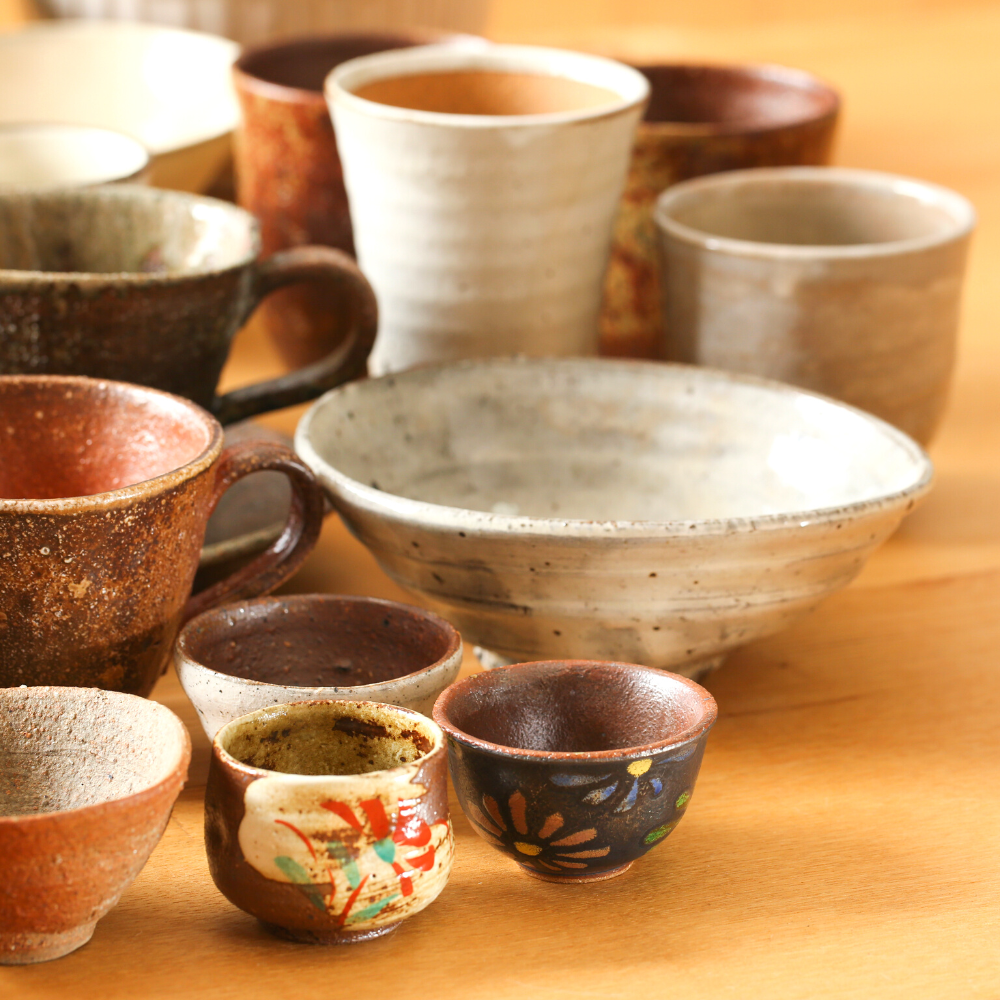
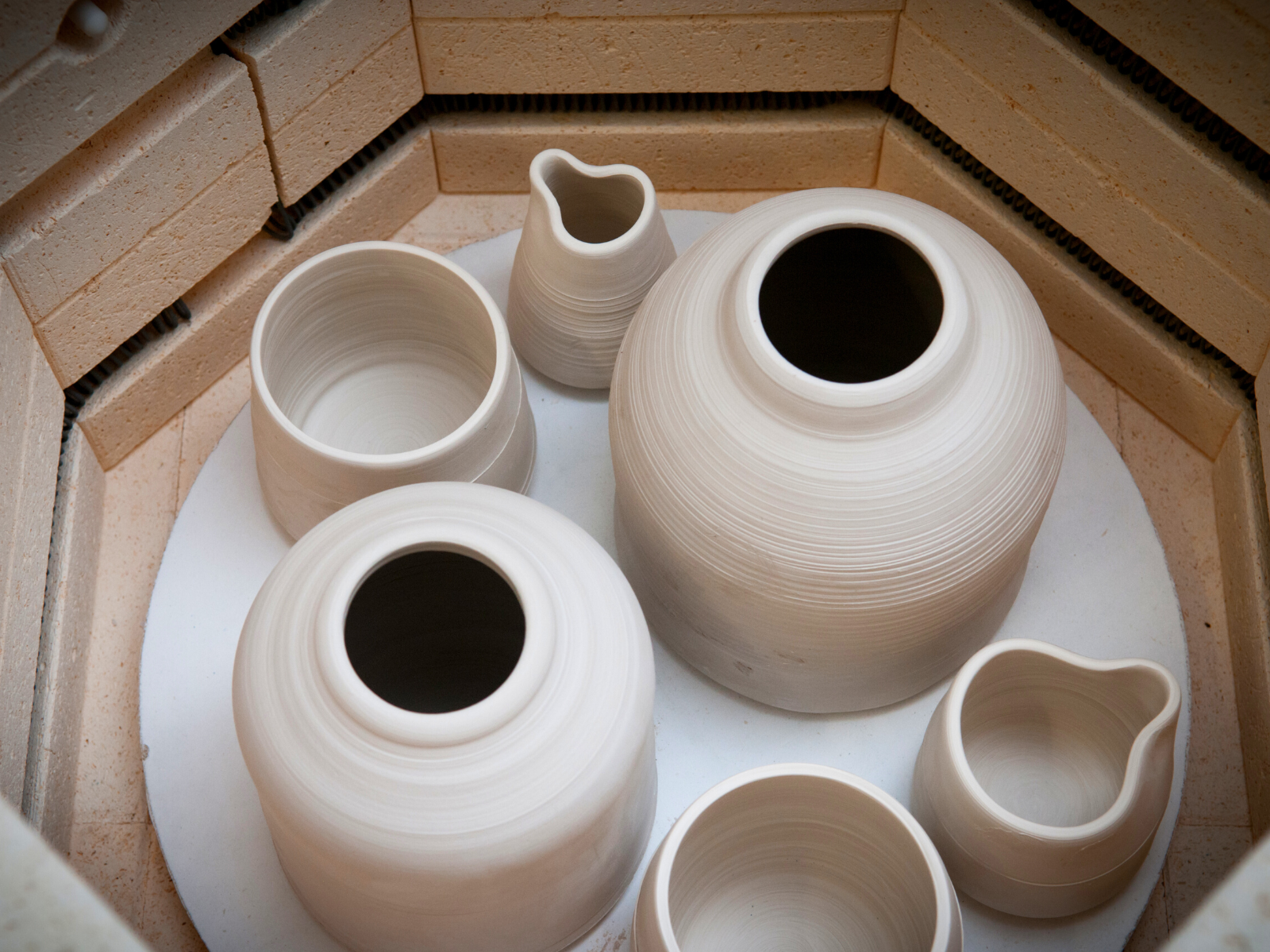
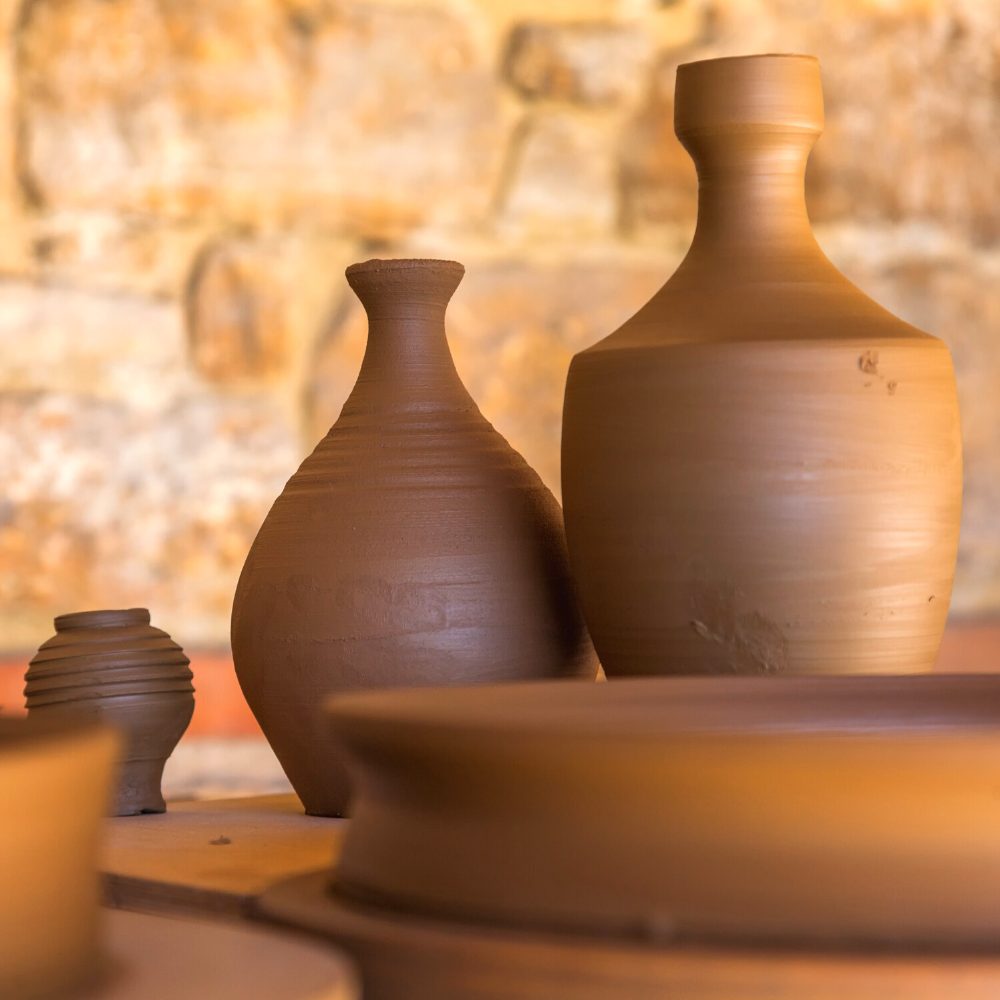



Earthenware: The Oldest Form of Pottery
Earthenware is the oldest and most common type of pottery.
It is made from earthenware clay that is fired at relatively low temperatures, typically between 1,000 and 1,150 degrees Celsius.
This type of clay is known for its porous nature, which means it must be glazed to hold liquids.
The presence of clay particles in earthenware clay, along with its high iron content, affects its vitrification and waterproofing properties, making it necessary to seal with glaze.
Earthenware is often used for making floor and wall tiles, as well as decorative pieces.
Earthenware clays are primarily composed of very fine minerals and organic matter, giving them a warm, earthy color.
These clays vary in their plasticity, making them suitable for both hand building and wheel throwing techniques.
The firing process for earthenware is less demanding than other types of pottery, making it an excellent choice for beginners.
Stoneware: Durable and Versatile
Stoneware is a type of pottery that is fired at higher temperatures, typically between 1,200 and 1,300 degrees Celsius.
This high-temperature firing results in a dense, non-porous material that is more durable than earthenware.
Fire clay, known for its high firing range and resistance to high temperatures, is often used in stoneware to enhance its durability and strength.
Stoneware clays are often used to create functional pottery, such as dinnerware and cookware, due to their strength and chip-resistant properties.
Stoneware clays contain a mix of fine minerals and organic matter, which gives them a speckled appearance.
These clays are more plastic than earthenware clays, making them easier to work with on the pottery wheel.
The firing process for stoneware requires high-tech kilns that can reach the necessary temperatures, ensuring the clay body vitrifies and becomes non-porous.
Porcelain: The Pinnacle of Pottery
Porcelain clay is considered the pinnacle of pottery due to its delicate appearance and high strength.
It is made from kaolin clays, also known as china clay, which are primarily composed of very fine minerals.
The high content of clay particles in porcelain clay makes it challenging for beginners, as it requires more water and has a tendency to become soft and collapse.
Porcelain clays are fired at extremely high temperatures, typically between 1,300 and 1,450 degrees Celsius, resulting in a translucent, non-porous material.
Porcelain clays are known for their unique properties, including their ability to be shaped into thin, delicate forms.
This type of clay is often used to create fine china and other high-end ceramic tableware.
The firing process for porcelain is demanding, requiring precise control of temperature and atmosphere to achieve the desired results.
Firing porcelain at high temperatures ensures the clay body becomes vitrified and non-porous, making it suitable for both functional and decorative pieces.
Bone China: A Blend of Strength and Elegance
Bone China is a type of porcelain that includes bone ash in its composition, giving it a unique combination of strength and translucency.
This type of pottery is fired at high temperatures, similar to true porcelain, but the addition of bone ash lowers the melting point and enhances the material's durability.
Bone China is often used to create high-quality tableware and decorative pieces.
The inclusion of bone ash in Bone China gives it a warm, ivory color and a smooth, glass-like finish.
This type of clay is highly plastic, making it suitable for intricate designs and detailed work.
The firing process for Bone China requires careful control of temperature and atmosphere to ensure the clay body vitrifies and achieves its characteristic translucency and strength.
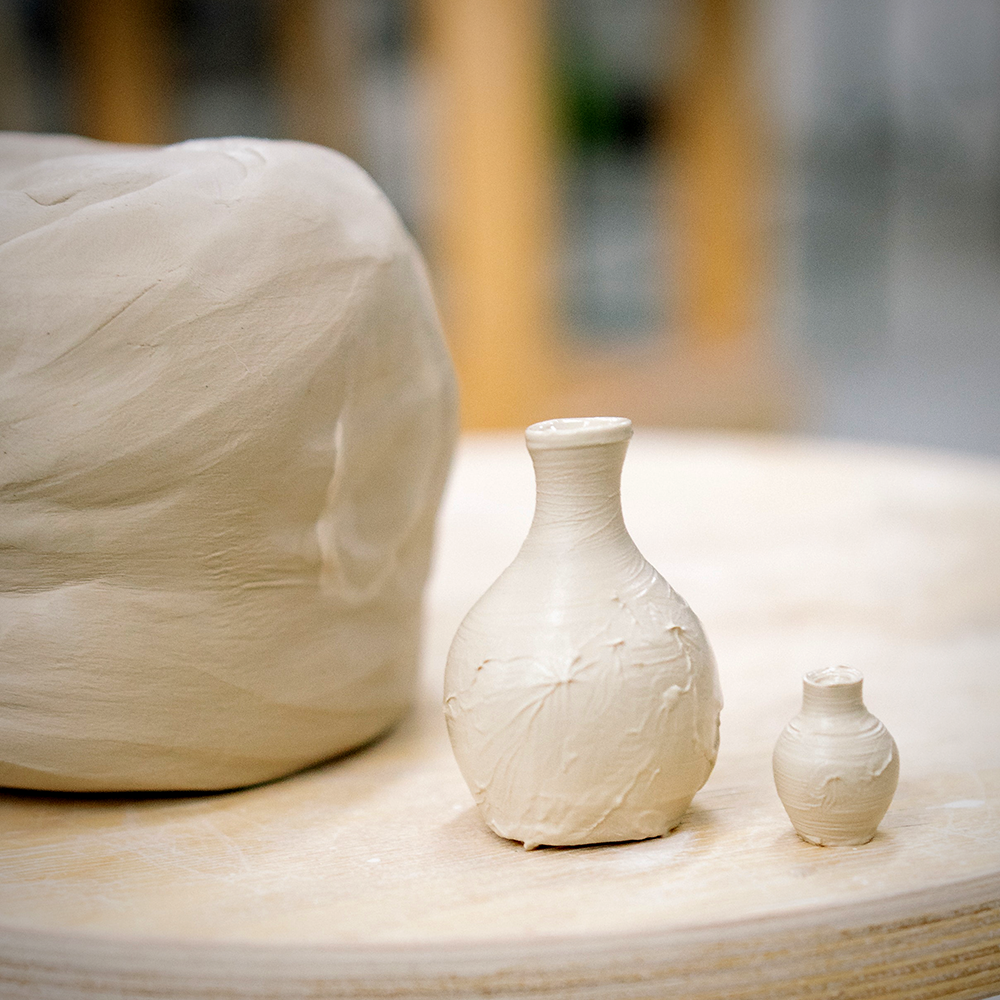
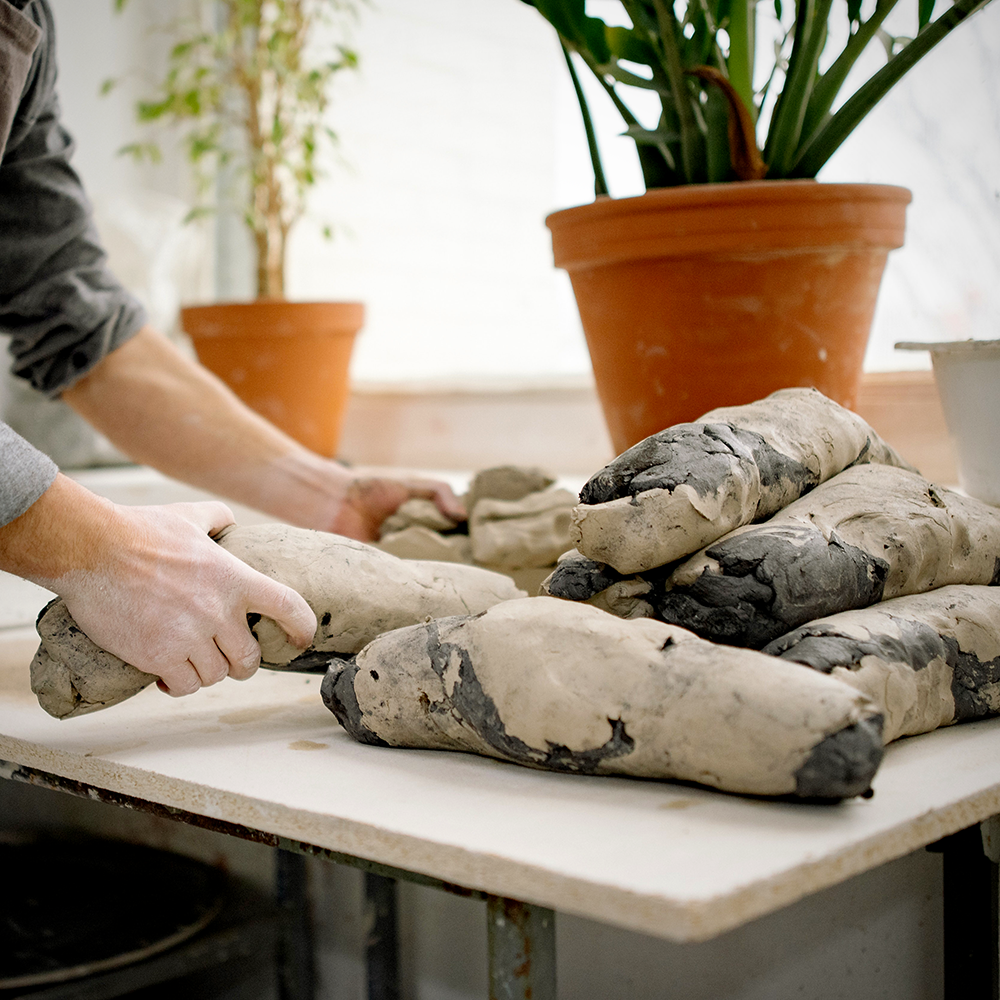



Firing Process: Transforming Clay into Pottery
The firing process is a critical step in pottery making, as it transforms raw clay into a durable, finished product.
There are two main stages in the firing process: bisque firing and glaze firing.
Bisque firing is the first stage, where the clay object is fired at a lower temperature to remove any remaining moisture and organic matter.
This process hardens the clay, making it easier to handle and ceramic glaze.
Glaze firing is the second stage, where the bisque-fired piece is coated with a glaze and fired at a higher temperature.
This process vitrifies the clay body and fuses the glaze to the surface, creating a smooth, glass-like finish.
The firing temperatures and techniques vary depending on the type of clay and the desired final product.
Types of Clay: Understanding the Raw Materials
Understanding the different types of pottery clay is essential for successful pottery making.
Clays vary in their composition, plasticity, and firing temperatures, making them suitable for different types of pottery.
Different clay bodies are used in pottery, including ball clays, which are known for their malleability and are often used in slip casting and as an addition to other clay bodies.
The four main types of clay used in pottery are earthenware clays, stoneware clays, porcelain clays, and ball clays.
Kaolin clay, a primary ingredient in porcelain, is white in color, withstands high temperatures, and becomes non-porous and very hard when fired, making it ideal for creating dinnerware and sculptural artistic work.
Earthenware clays are low-fire clays that are easy to work with and ideal for beginners.
Stoneware clays are mid- to high-fire clays that are durable and versatile, making them suitable for functional pottery.
Porcelain clays are high-fire clays that are known for their strength and translucency, making them ideal for fine china and decorative pieces.
Ball clays are highly plastic clays that are often used to improve the workability of other clay bodies.
Plastic Clay: The Workhorse of Pottery
Plastic clay is a term used to describe clays that are highly workable and easy to shape.
These clays are ideal for wheel throwing and hand building techniques, as they can be easily manipulated without cracking or breaking.
Plastic clays are often used in pottery projects that require intricate designs and detailed work.
Plastic and polymer clays are primarily composed of fine minerals and organic matter, giving them a smooth, pliable texture.
These clays are often mixed with other clays to improve their workability and plasticity.
The firing process for plastic clays varies depending on the type of clay and the desired final product.
Air Dry Clay: A Convenient Alternative
Air dry clay is a type of clay that does not require firing in a kiln to harden.
This type of clay is ideal for beginners and hobbyists, as it can be easily shaped and left to dry at room temperature.
Air dry clay is often used for small pottery projects and decorative pieces that do not need to be functional.
Air dry clay is made from a combination of natural clays and synthetic materials, giving it a smooth, pliable texture.
This type of clay is easy to work with and can be painted or glazed once dry.
While air dry clay is not as durable as fired clay, it is a convenient alternative for those who do not have access to a kiln.



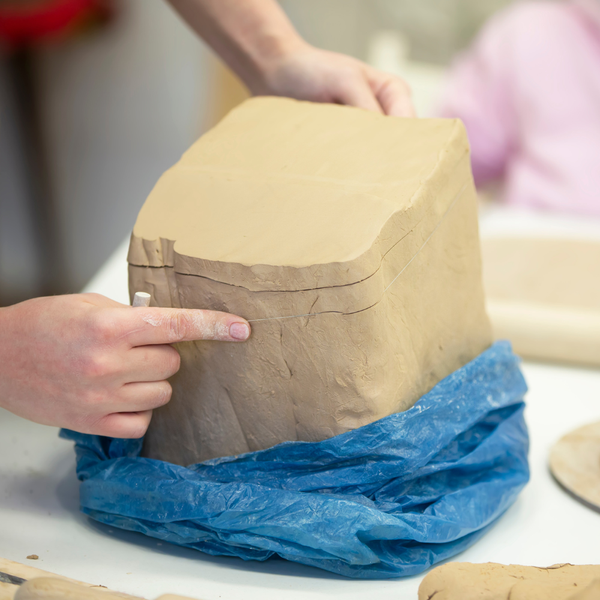
Hand Building: The Art of Shaping Clay by Hand
Hand building is a traditional pottery technique that involves shaping clay by hand without the use of a pottery wheel.
This technique is ideal for creating unique, one-of-a-kind pieces, as it allows for greater control and creativity.
Hand building techniques include pinching, coiling, and slab building.
Pinching involves shaping the clay by pinching it between the fingers, creating small, delicate forms.
Coiling involves rolling the clay into long, thin coils and stacking them to create larger forms.
Slab building involves rolling the clay into flat slabs and cutting and assembling them to create geometric shapes.
Hand building is a versatile technique that can be used to create both functional and decorative pieces.
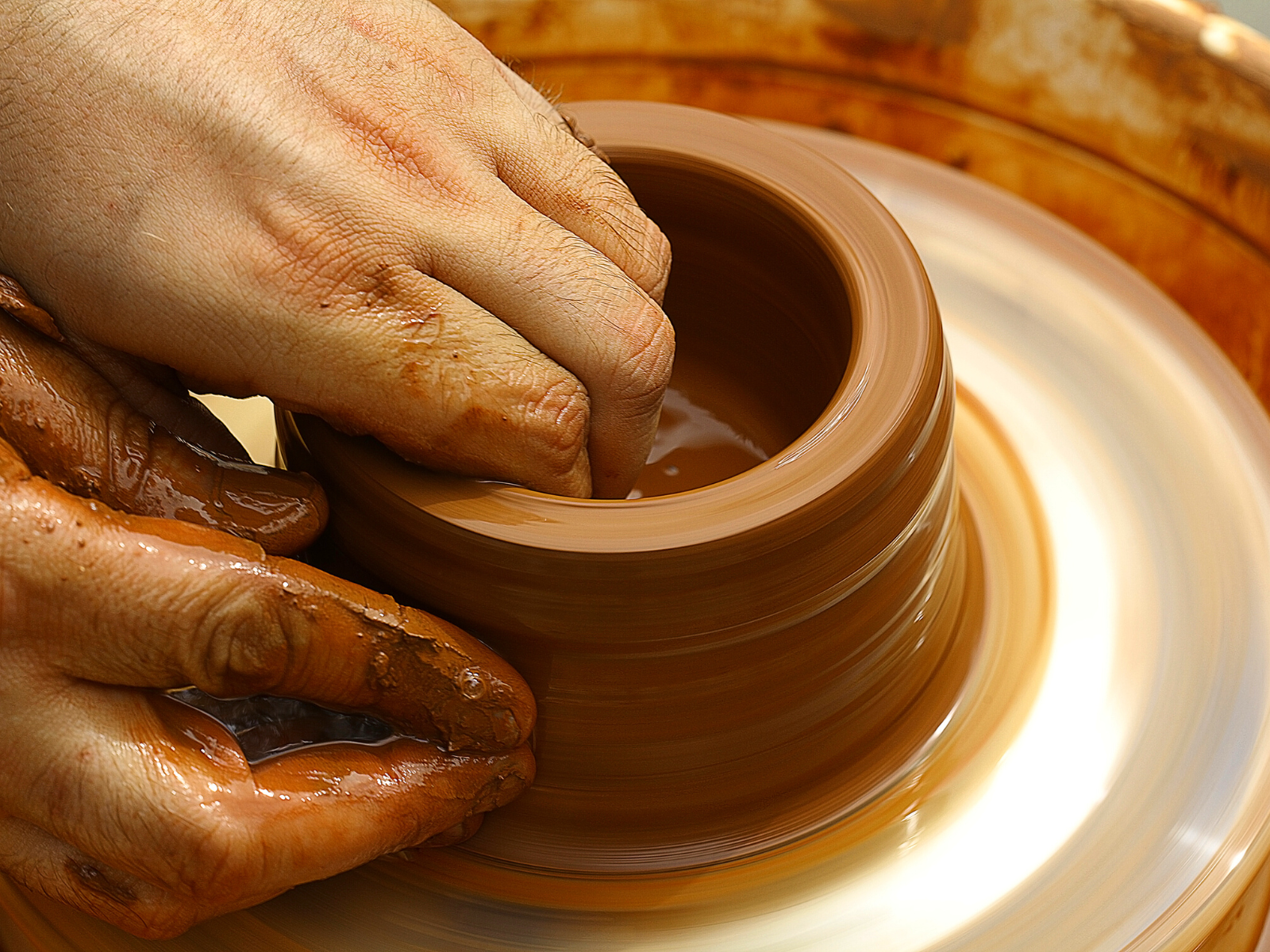
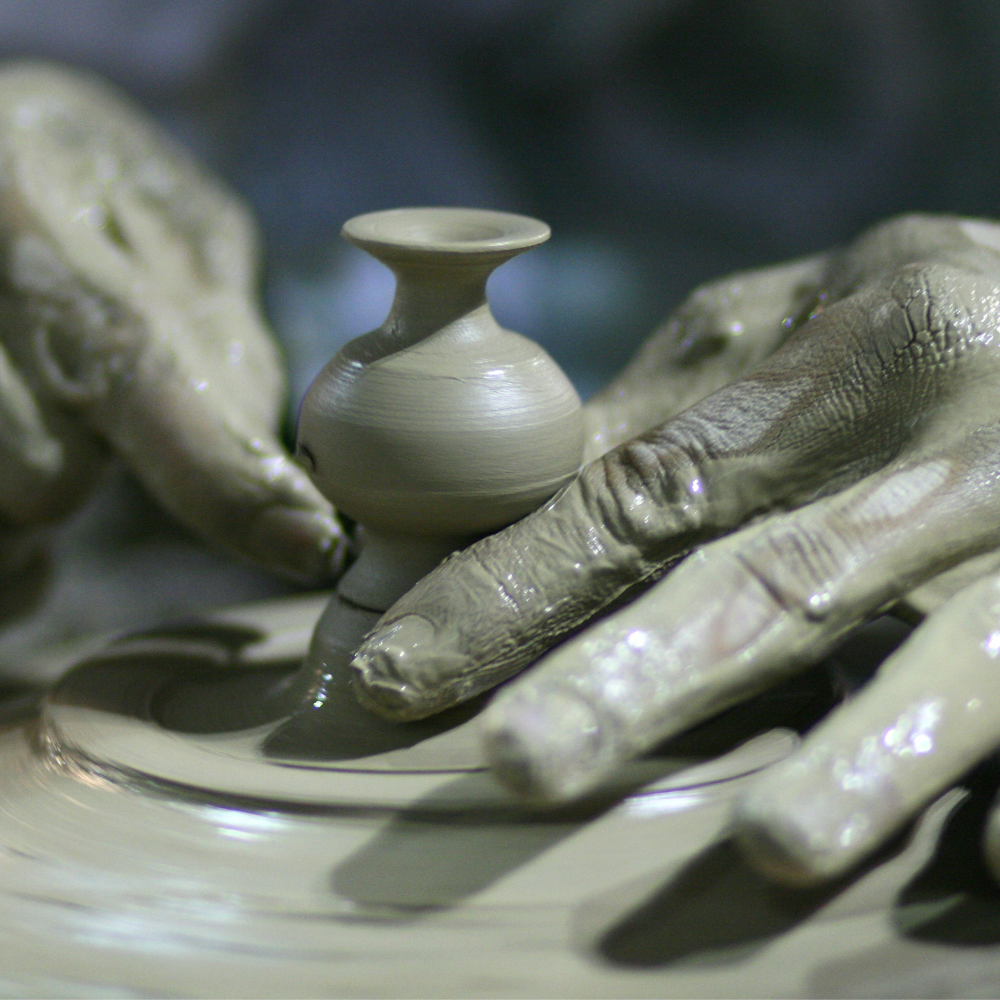
Wheel Throwing: Mastering the Pottery Wheel
Wheel throwing is a pottery technique that involves shaping clay on a rotating pottery wheel.
This technique is ideal for creating symmetrical, uniform pieces, such as bowls, vases, and plates.
Wheel throwing requires a high level of skill and practice, as it involves controlling the speed and pressure of the wheel to shape the clay.
The process of wheel throwing begins with centering the clay on the wheel, which involves pressing and shaping the clay into a symmetrical form.
Once the clay is centered, the potter uses their hands and tools to shape the clay into the desired form.
Wheel throwing is a challenging but rewarding technique that allows for the creation of precise, functional pieces.
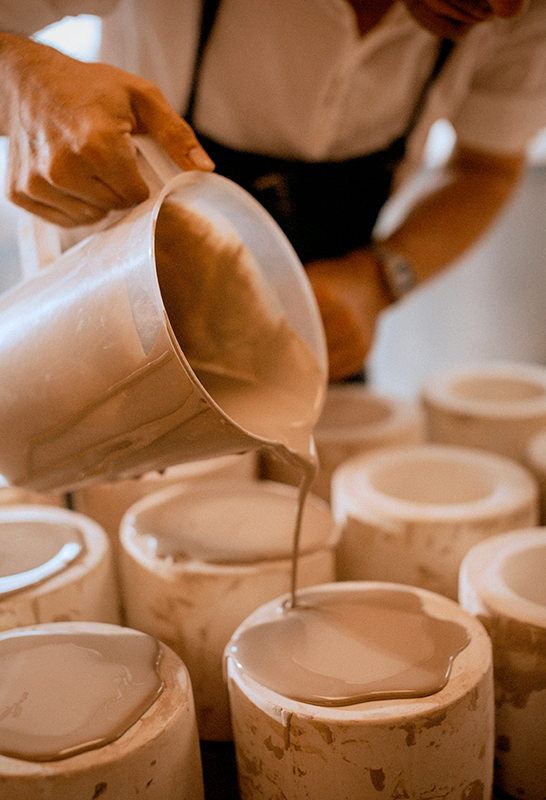
Slip Casting: Creating Intricate Designs
Slip casting is a pottery technique that involves pouring liquid clay, or slip, into a plaster mold.
This technique is ideal for creating intricate designs and detailed work, as the slip takes on the shape of the mold.
Slip casting is often used to create fine china and other high-end ceramic tableware.
The process of slip casting begins with creating a plaster mold of the desired form.
The mold is then filled with liquid clay, or slip, and left to set.
Once the slip has hardened, the mold is removed, and the piece is fired in a kiln.
Slip casting allows for the creation of precise, detailed pieces that would be difficult to achieve with other techniques.


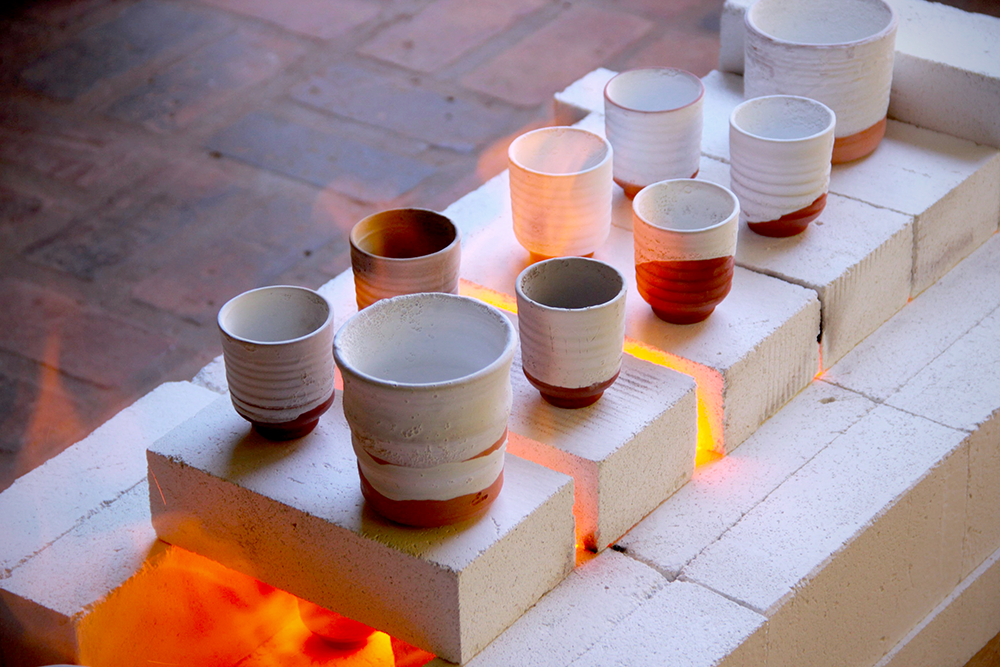
Bisque Firing: First Step in the Firing Process
Bisque firing is the first stage in the firing process, where the clay object is fired at a lower temperature to remove any remaining moisture and organic matter.
This process hardens the clay, making it easier to handle and glaze.
Bisque firing is an essential step in pottery making, as it prepares the clay for the final glaze firing.
The bisque firing process typically takes place at temperatures between 900 and 1,000 degrees Celsius.
The clay object is placed in a kiln and slowly heated to the desired temperature, allowing any remaining moisture and organic matter to burn off.
Once the bisque firing is complete, the clay object is ready for glazing and the final glaze firing.
Glaze Firing: Adding the Finishing Touch
Glaze firing is the second stage in the firing process, where the bisque-fired piece is coated with a glaze and fired at a higher temperature.
This process vitrifies the clay body and fuses the glaze to the surface, creating a smooth, glass-like finish.
Glaze firing is an essential step in pottery making, as it adds the finishing touch to the piece.
The glaze firing process typically takes place at temperatures between 1,200 and 1,300 degrees Celsius.
The bisque-fired piece is coated with a glaze and placed in a kiln, where it is slowly heated to the desired temperature.
The glaze melts and fuses to the surface of the clay, creating a smooth, glass-like finish.
Once the glaze firing is complete, the piece is ready for use or display.
High Temperature Firing: Durability and Strength
High temperature firing is a critical step in the pottery making process, as it ensures the clay body becomes vitrified and achieves its maximum strength and durability.
This process is essential for creating functional pottery, such as dinnerware and cookware, as it ensures the pieces are non-porous and chip-resistant.
High temperature firing typically takes place at temperatures between 1,200 and 1,450 degrees Celsius, depending on the type of clay and the desired final product.
The clay object is placed in a kiln and slowly heated to the desired temperature, allowing the clay body to vitrify and achieve its maximum strength and durability.
High temperature firing is essential for creating durable, functional pottery that can withstand everyday use.
Low Temperature Firing: Creating Warm, Earthy Tones
Low temperature firing is a pottery technique that involves firing clay at lower temperatures, typically between 900 and 1,150 degrees Celsius.
This process is often used for earthenware and other low-fire clays, as it creates warm, earthy tones and a porous, non-vitrified clay body.
Low temperature firing is ideal for creating decorative pieces and pottery that does not need to be functional.
The lower firing temperatures allow for greater control over the final color and texture of the piece, creating unique, one-of-a-kind designs.
Low temperature firing is a versatile technique that can be used to create a wide range of pottery styles and finishes.
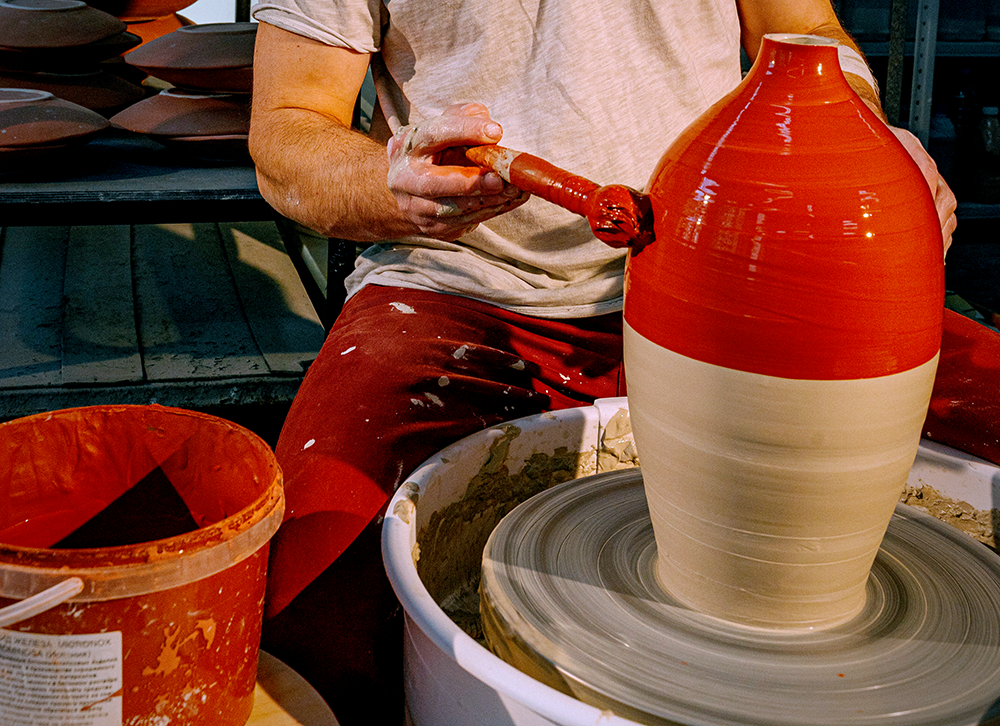
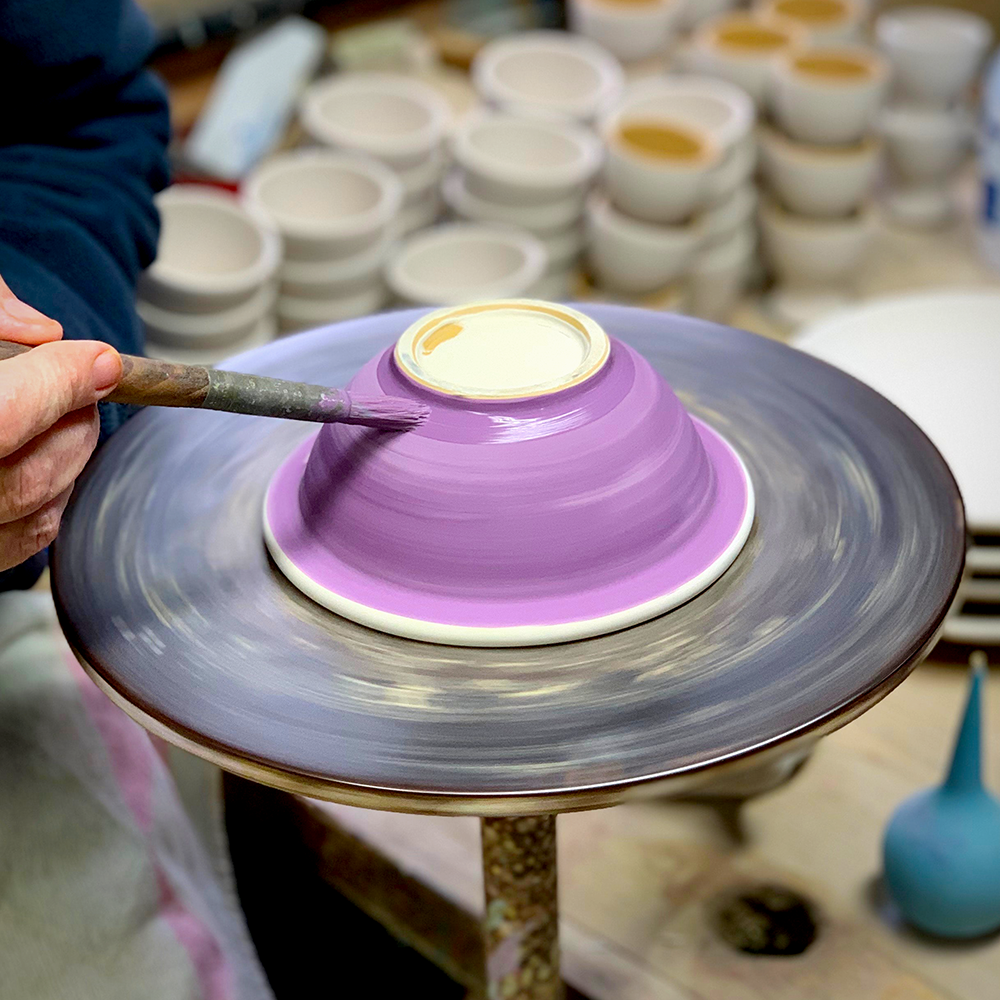
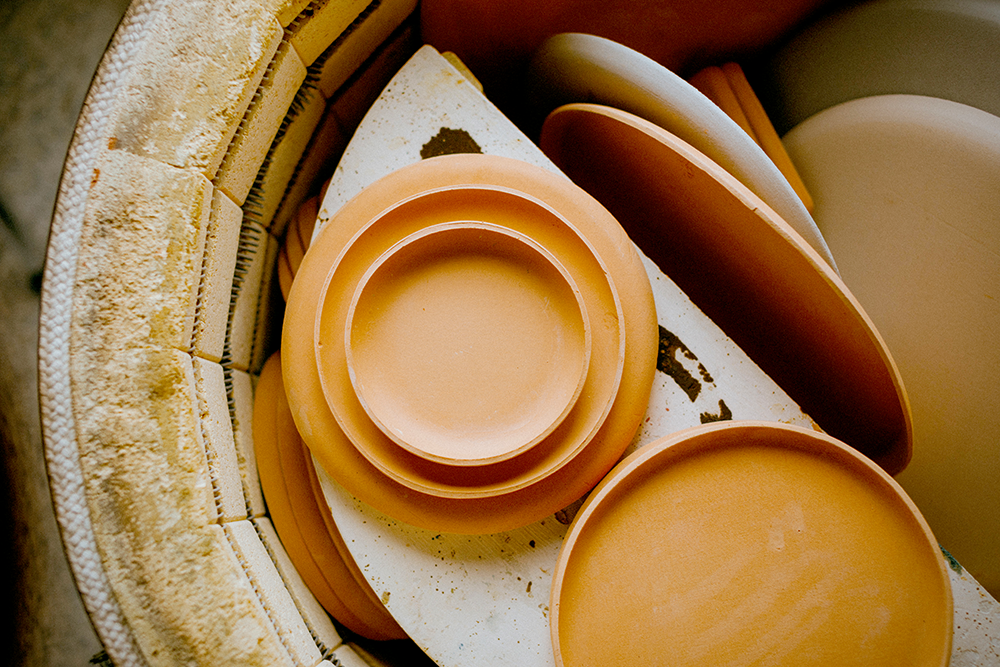



Choosing the Correct Clay: Factors to Consider
Choosing the correct clay is essential for successful pottery making, as different clays have unique properties and firing requirements.
Factors to consider when selecting a clay include the type of pottery you want to create, the firing temperatures required, and the workability of the clay.
Earthenware clays are ideal for beginners and low-fire pottery, as they are easy to work with and fire at lower temperatures.
Stoneware clays are suitable for functional pottery, as they are durable and fire at higher temperatures.
Porcelain clays are ideal for fine china and decorative pieces, as they are strong and translucent. Kaolin clay, the primary ingredient in porcelain, is white in color, withstands high temperatures, and becomes non-porous and very hard when fired.
Ball clays are highly plastic and can be mixed with other clays to improve workability.
Functional Pottery: Creating Everyday Items
Functional pottery refers to pottery that is designed for everyday use, such as dinnerware, cookware, and storage containers.
This type of pottery must be durable, non-porous, and able to withstand everyday use.
Functional pottery is often made from stoneware or porcelain clays, as these clays are strong and chip-resistant.
Creating functional pottery requires careful consideration of the clay body, firing temperatures, and glaze.
The clay body must be durable and able to withstand high temperatures, while the glaze must be non-toxic and food-safe.
Functional pottery is a rewarding and practical aspect of pottery making, as it allows you to create items that can be used and enjoyed every day.
Decorative Pottery and Artistic Expression
Decorative pottery refers to pottery that is designed for aesthetic purposes, such as vases, sculptures, and wall art.
This type of pottery allows for greater artistic expression and creativity, as it does not need to be functional.
Decorative pottery can be made from a wide range of clays, including earthenware, stoneware, and porcelain.
Creating decorative pottery involves experimenting with different techniques, glazes, and finishes to achieve the desired look.
The firing process for decorative pottery can vary depending on the type of clay and the desired final product.
Decorative pottery is a versatile and creative aspect of pottery making, allowing you to showcase your artistic skills and create unique, one-of-a-kind pieces.
Modern Techniques and Innovations
Pottery today has evolved significantly from its ancient origins, with modern techniques and innovations transforming the craft.
High-tech kilns, advanced glazing techniques, and new types of clay have expanded the possibilities for pottery making, allowing for greater precision and creativity.
Modern pottery techniques include slip casting, 3D printing, and digital glazing, which allow for the creation of intricate designs and detailed work.
High-tech kilns and firing techniques ensure precise control over temperature and atmosphere, resulting in consistent, high-quality results.
Pottery today is a dynamic and ever-evolving craft, with new techniques and innovations continually pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
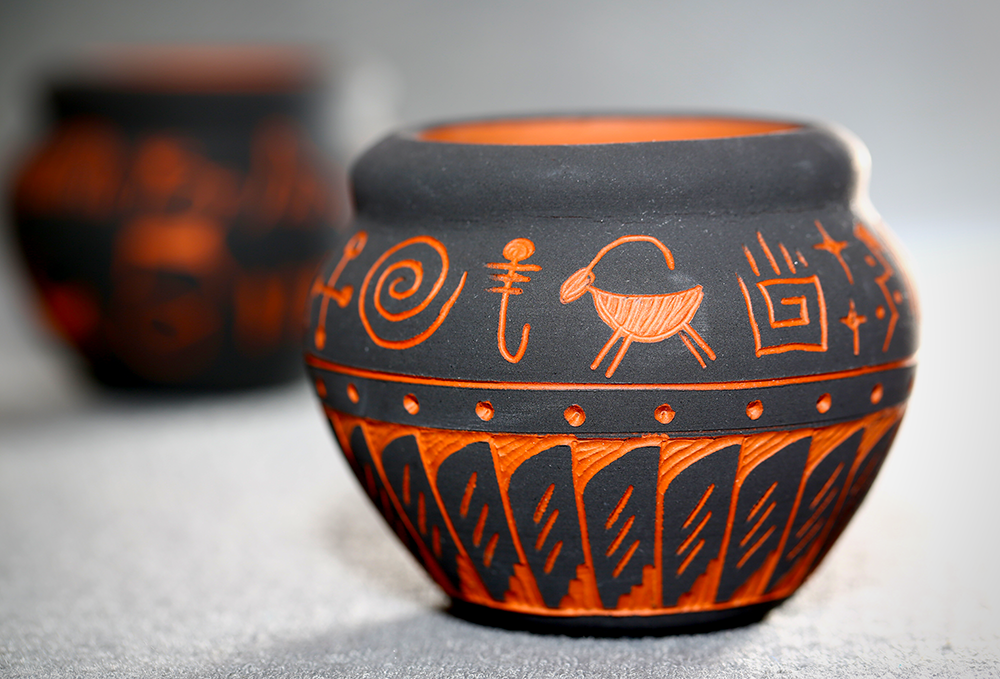



Embrace the Endless Possibilities of Pottery
Pottery is more than just a craft; it's a journey through history, creativity, and innovation.
From the humble beginnings of Earthenware to the refined elegance of Bone China, each type of pottery offers unique opportunities for artistic expression and functional design.
By mastering the properties of different clays and the intricacies of the firing process, you can unlock a world of endless possibilities.
Whether you're a seasoned artisan or a curious beginner, the timeless art of pottery making invites you to explore, create, and leave your mark on this ancient yet ever-evolving craft.
Dive in, and let your imagination shape the clay into something extraordinary.
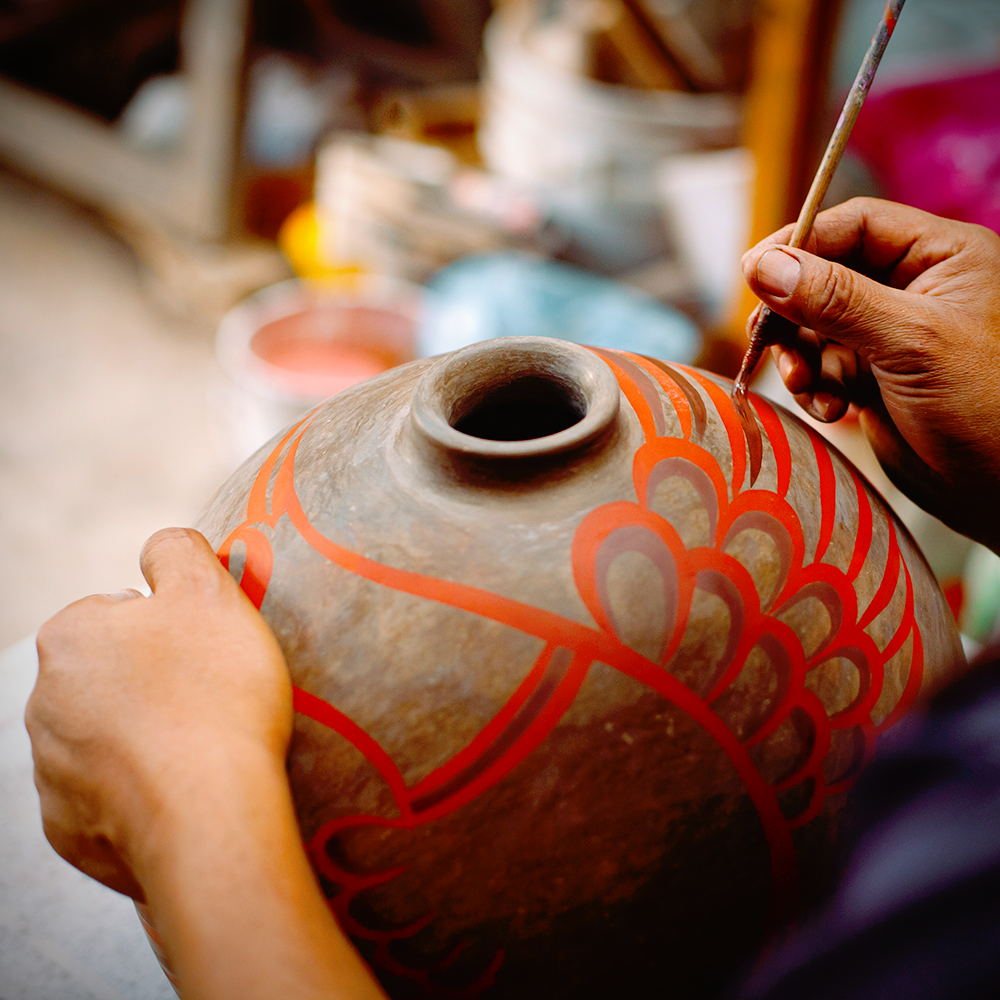



Pottery FAQs
Are you ready to dive into the fascinating world of pottery?
Whether you're a seasoned potter or just starting out, understanding the basics can make all the difference.
From the different types of pottery to the intricate firing process, and even how to choose the right clay, we've got you covered.
Let's unravel the mysteries of pottery with these frequently asked questions!
What are the four types of pottery?
The four types of pottery are Earthenware, Stoneware, Porcelain, and Bone China. Each type has unique characteristics, firing temperatures, and uses.
What is the firing process in pottery making?
The firing process in pottery making involves two main stages: bisque firing and glaze firing. Bisque firing hardens the clay and removes moisture, while glaze firing vitrifies the clay body and fuses the glaze to the surface.
What factors should be considered when choosing clay for pottery?
When choosing clay for pottery, consider the type of pottery you want to create, the firing temperatures required, and the workability of the clay. Different clays have unique properties and firing requirements, making them suitable for different types of pottery.
What tools are essential for pottery making?
Essential tools for pottery making include a potter's wheel, kiln, clay, trimming tools, sponges, ribs, and a variety of brushes. These pottery tools help shape, refine, and finish your pottery pieces.
How do you prevent pottery from cracking during drying?
To prevent pottery from cracking during drying, ensure even thickness throughout the piece, dry it slowly and evenly, and cover it with plastic to control the drying rate. Avoid exposing it to direct sunlight or drafts.
What is the difference between hand-building and wheel-throwing?
Hand-building involves creating pottery using hands and simple tools, allowing for more organic and unique shapes. Wheel-throwing uses a potter's wheel to shape the clay, offering more symmetrical and refined forms.
Can you recycle clay in pottery making?
Yes, clay can be recycled in pottery making. Dry scraps can be rehydrated and wedged to remove air bubbles, making the clay reusable. This process is both economical and environmentally friendly.
What is glazing in pottery, and why is it important?
Glazing is the process of applying a glassy coating to pottery to seal and decorate it. It enhances the piece's aesthetic appeal, makes it waterproof, and adds durability.
How do you choose the right glaze for your pottery?
When choosing a glaze, consider the type of clay, the firing temperature, and the desired finish. Test glazes on small pieces first to see how they react with your clay and firing conditions.
What safety precautions should be taken when working with pottery?
Safety precautions include wearing a mask to avoid inhaling clay dust, using gloves when handling glazes and chemicals, ensuring proper ventilation in the workspace, and keeping tools and equipment clean.
What are some common pottery techniques?
Common pottery techniques include coiling, slab building, pinch pots, and wheel throwing. Each technique offers different ways to shape and create unique pottery pieces.
How do you fix cracks or imperfections in pottery?
To fix cracks or imperfections, use a mixture of clay and water called slip to fill in the cracks. For larger cracks, reinforce with additional clay and smooth out the surface before firing.
What is the significance of wedging clay?
Wedging clay is the process of kneading it to remove air bubbles and ensure a uniform consistency. This step is crucial to prevent cracking and ensure the clay is workable.
What are some tips for beginners in pottery?
Some ceramics tips for beginners: start with simple projects, practice basic techniques, be patient, and don't be afraid to make mistakes. Joining a pottery class or community can also provide valuable guidance and support.
What is the role of temperature in pottery firing?
Temperature plays a critical role in pottery firing. Different clays and glazes require specific temperatures to achieve the desired hardness, durability, and finish. Monitoring and controlling the kiln temperature is essential for successful firing.
How do you create texture in pottery?
Texture can be created using various tools such as stamps, carving tools, and textured rollers. Experimenting with different techniques like impressing, incising, and adding slip can also add unique textures to your pottery.
What is the importance of trimming in pottery?
Trimming is important for refining the shape, removing excess clay, and creating a smooth, even surface. It also helps in achieving a balanced and professional-looking finished piece.
How do you maintain and care for pottery tools?
Maintain and care for pottery tools by cleaning them after each use, storing them in a dry place, and regularly inspecting for wear and tear. Proper care extends the life of your tools and ensures better results in your pottery projects.



Eager to learn more about the stages of clay? Check out Jonthepotter's video!
Want even more content about creativity and art?
Be sure to check out all of our creative chronicles!
Love pottery and working with clay?
Check out some of our other ceramic articles:
-What is the difference between ceramics and pottery?
-How do you identify ceramics?
-What is Italian pottery called?
-What are the 5 methods of working with clay?
-What is the difference between hand building and throwing clay?










