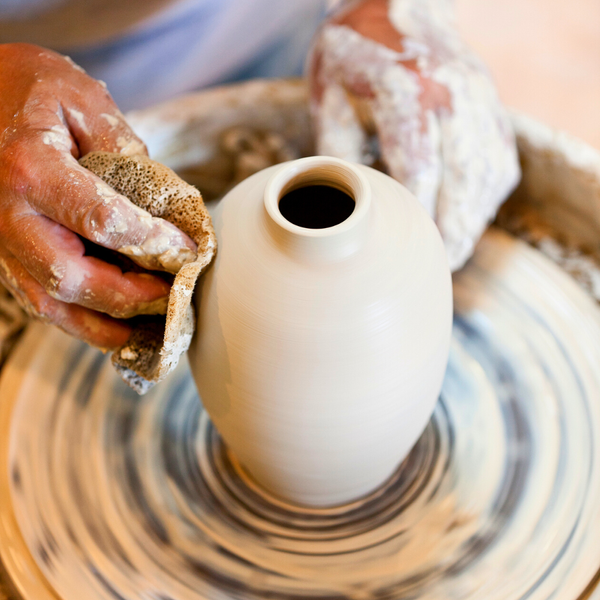
Are you ready to embark on a journey through the captivating world of ceramic arts?
Understanding the difference between ceramics and pottery is essential for anyone passionate about these age-old crafts.
While often used interchangeably, these terms hold unique meanings and applications.
Join us as we delve into the nuances that set ceramics and pottery apart, exploring their materials, techniques, and uses.
Get ready to elevate your knowledge and appreciation for these timeless arts!
Key Takeaways:
- Ceramics and Pottery Defined: Pottery and ceramics are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings. Pottery specifically refers to objects made from clay and fired at high temperatures, while ceramics encompass a broader category of objects made from non-metallic, inorganic materials.
- Material and Techniques: Pottery primarily uses earthenware, stoneware, and porcelain clays, whereas ceramics can include other non-metallic materials.
- Applications and Uses: Pottery is often functional, such as bowls and vases, while ceramics can be both functional and decorative, including tiles and sculptures.
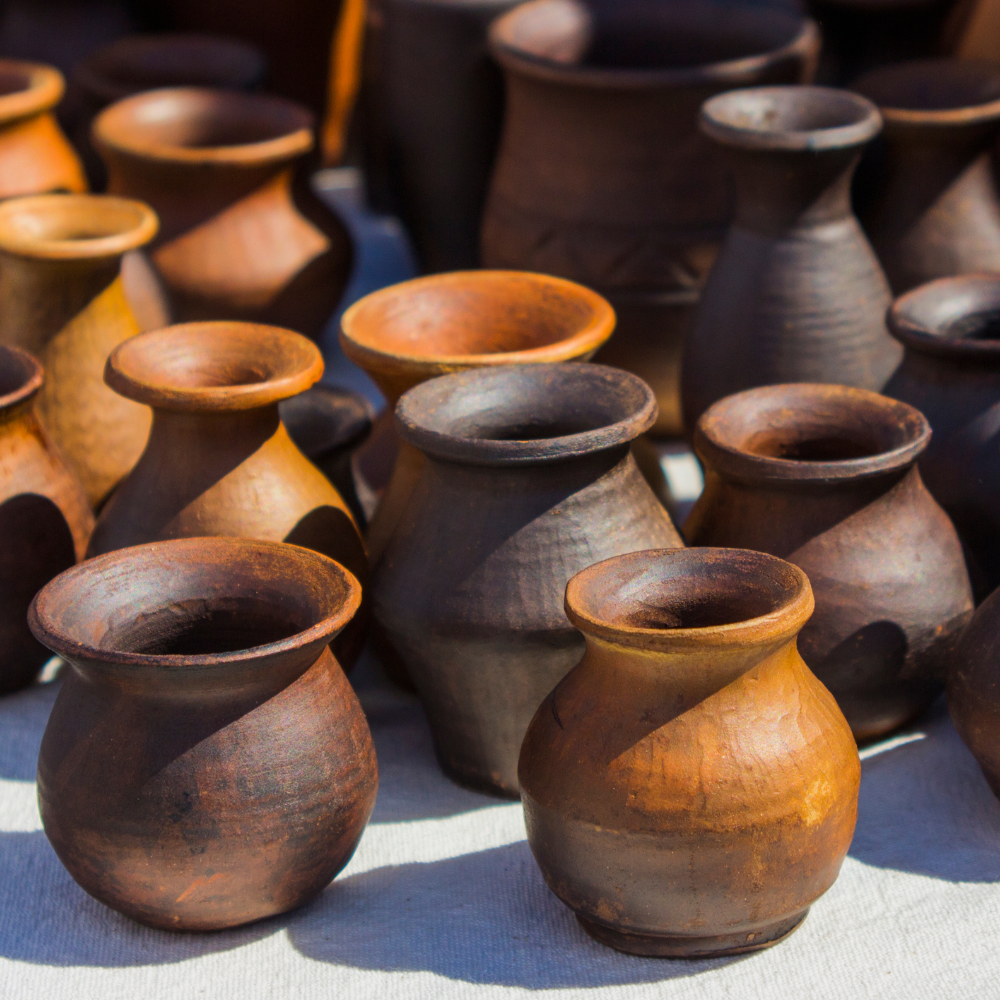


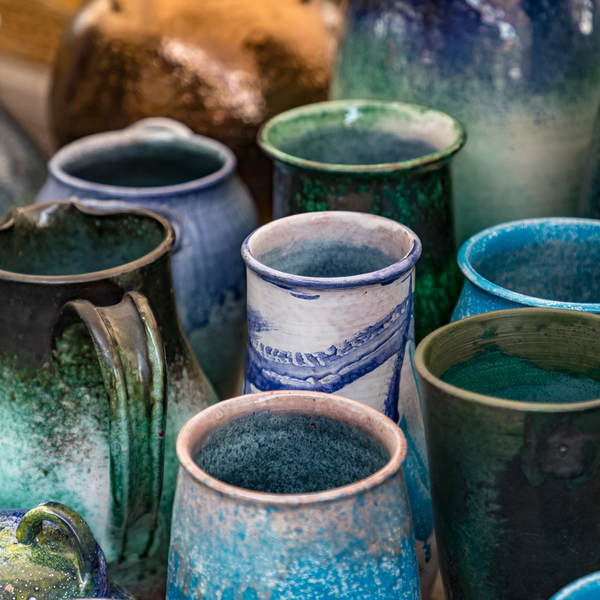
Ceramics: A Broad Spectrum
Ceramics refer to objects made from non-metallic materials that are permanently changed when heated.
This category includes a wide range of items, from fine china to engineering components.
Ceramic materials include a variety of substances such as clay, glaze, porcelain, stoneware, and earthenware.
The word ceramic originates from the Greek word “keramos,” meaning potter’s clay.
Ceramics are known for their durability and versatility, making them suitable for both artistic and functional purposes.
Ceramic objects can be created using various techniques, including wheel throwing, slab construction, and casting.
These methods allow ceramic artists to produce everything from delicate porcelain figurines to robust wall tiles.
The firing process, which involves heating the clay to high temperatures, is essential for transforming the raw material into a durable ceramic piece.
Pottery: A Subset of Ceramics
Pottery, on the other hand, specifically refers to items made from clay and fired at high temperatures.
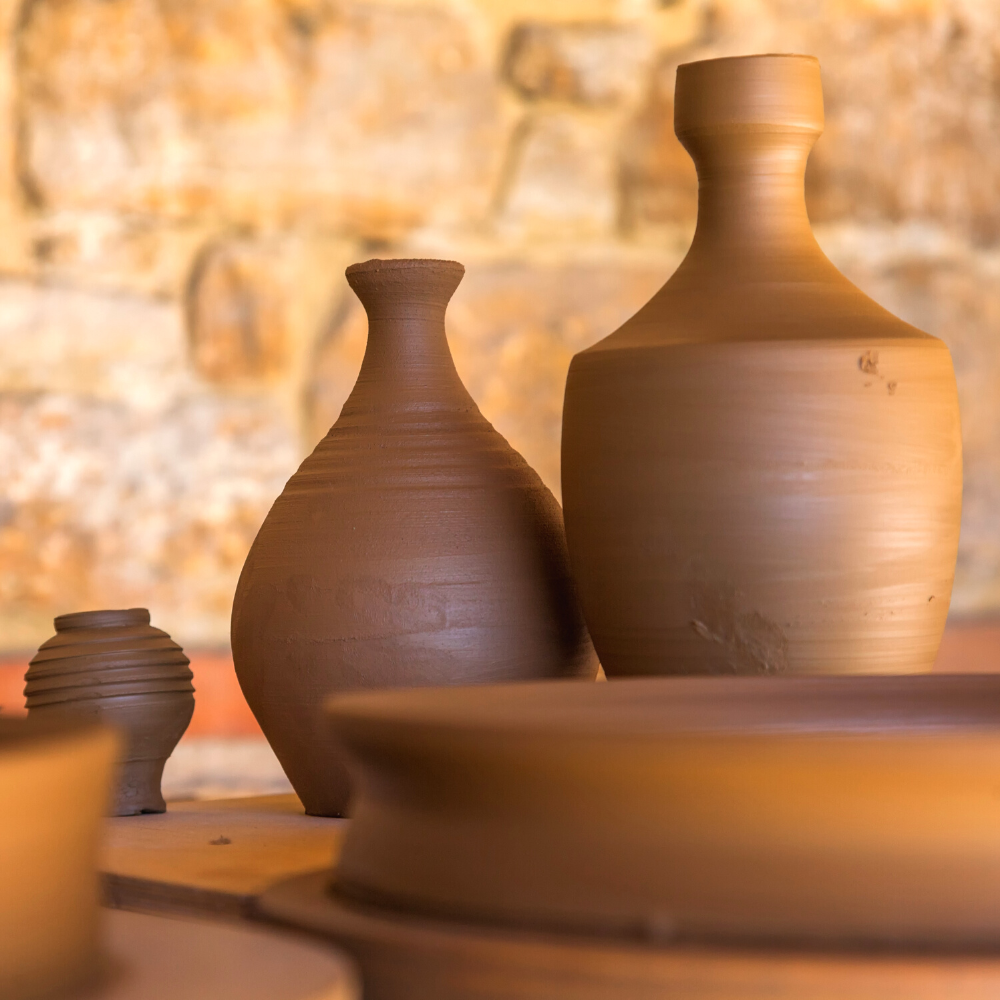
Ceramic pottery includes functional items made from clay, such as coffee mugs and vases.
The word pottery is derived from the Latin word “potium,” meaning drinking vessel.
Pottery is one of the oldest human crafts, with a history dating back thousands of years.
It includes functional objects like bowls, vases, and flower pots, as well as decorative items.
Pottery is typically made using three main types of clay: earthenware, stoneware, and porcelain.
Each type of clay has unique properties that affect the final product.
For example, earthenware clay is a low fire clay that is porous and less durable than stoneware or porcelain.
Stoneware clay, fired at higher temperatures, is non-porous and more durable.
Porcelain clay, known for its fine white color and translucency, is used to create fine china and other high-quality items.
Materials Used in Ceramics
Ceramics can be made from a variety of materials, including clay, glass, and other non-metallic substances.
Ceramic material refers to substances that are permanently changed when heated, such as clay and glass.
The primary clay used in ceramics is composed of fine particles that can be molded and shaped.
Other elements, such as feldspar minerals and iron oxide, are often added to enhance the properties of the clay.
In addition to traditional ceramics, modern ceramics can include advanced materials used for engineering purposes.
These materials are designed to withstand extreme conditions and are used in applications such as aerospace and electronics.
The versatility of ceramics makes them suitable for a wide range of uses, from everyday household items to specialized industrial components.
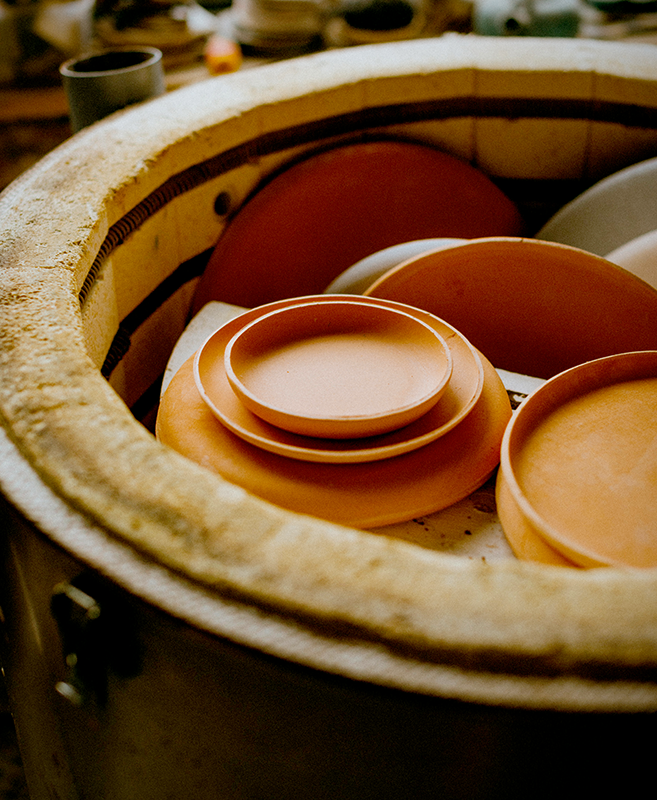
Types of Clay in Pottery: Earthenware Clay
Pottery primarily uses three types of clay: earthenware, stoneware, and porcelain.
Earthenware clay is a low fire clay that is easy to work with but less durable than other types.
It is often used for making decorative objects and low fire pottery.
Stoneware clay, fired at higher temperatures, is more durable and non-porous, making it suitable for functional objects like dinnerware and cookware.
Ball clay is often used in stoneware clay blends and has historical significance in the production of floor and wall tiles.
Porcelain clay, also known as fine white clay, is prized for its translucency and strength.
It is used to create fine china and other high-quality ceramic items. Bone china, a type of porcelain, contains bone ash, which gives it a unique translucency and strength.
Each type of clay has specific properties that make it suitable for different applications, allowing potters to choose the best material for their projects.
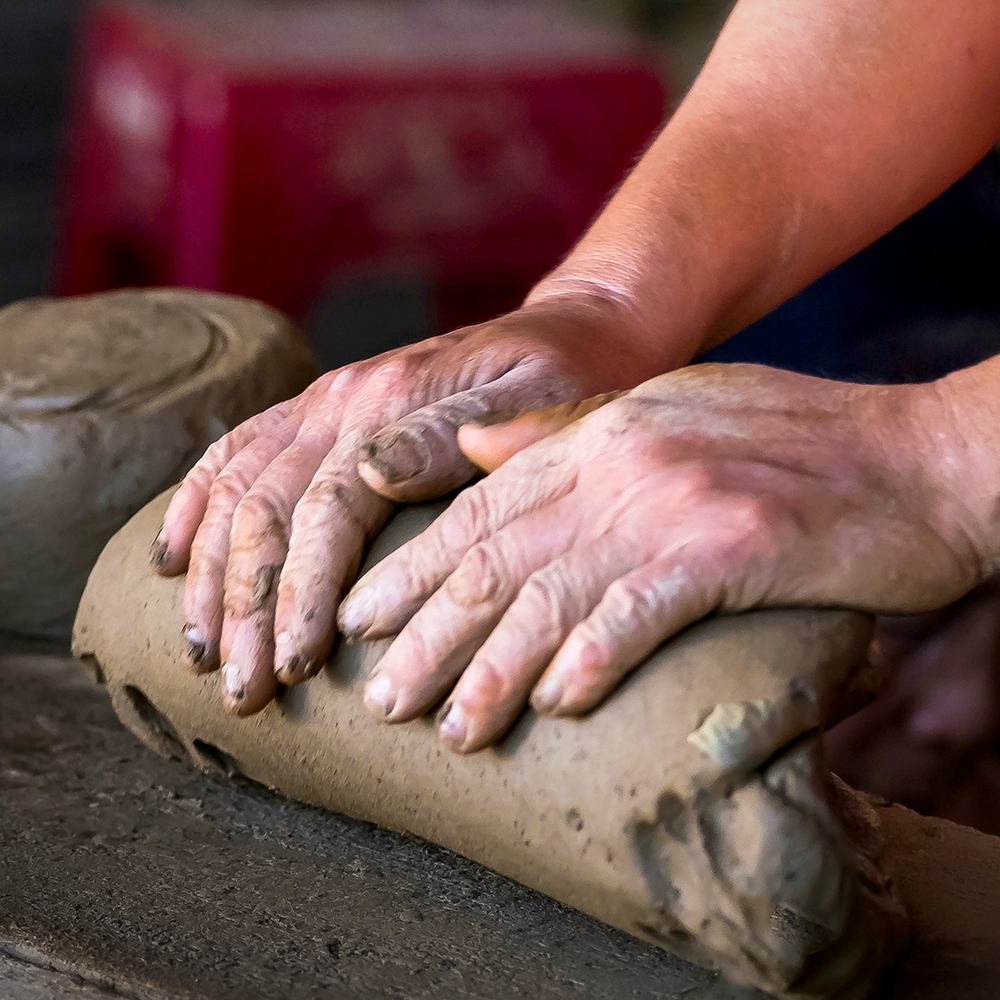
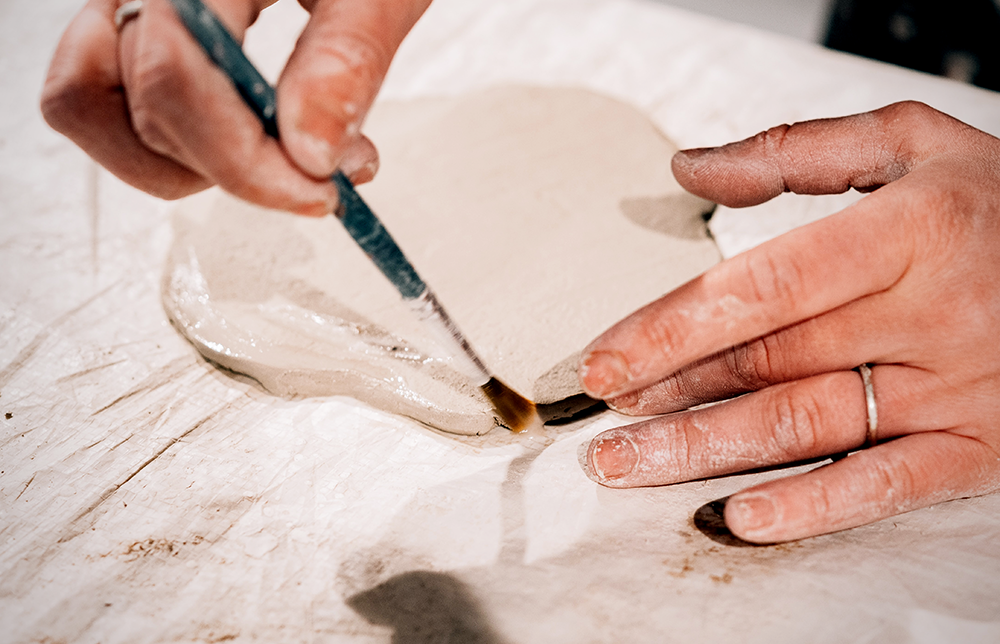
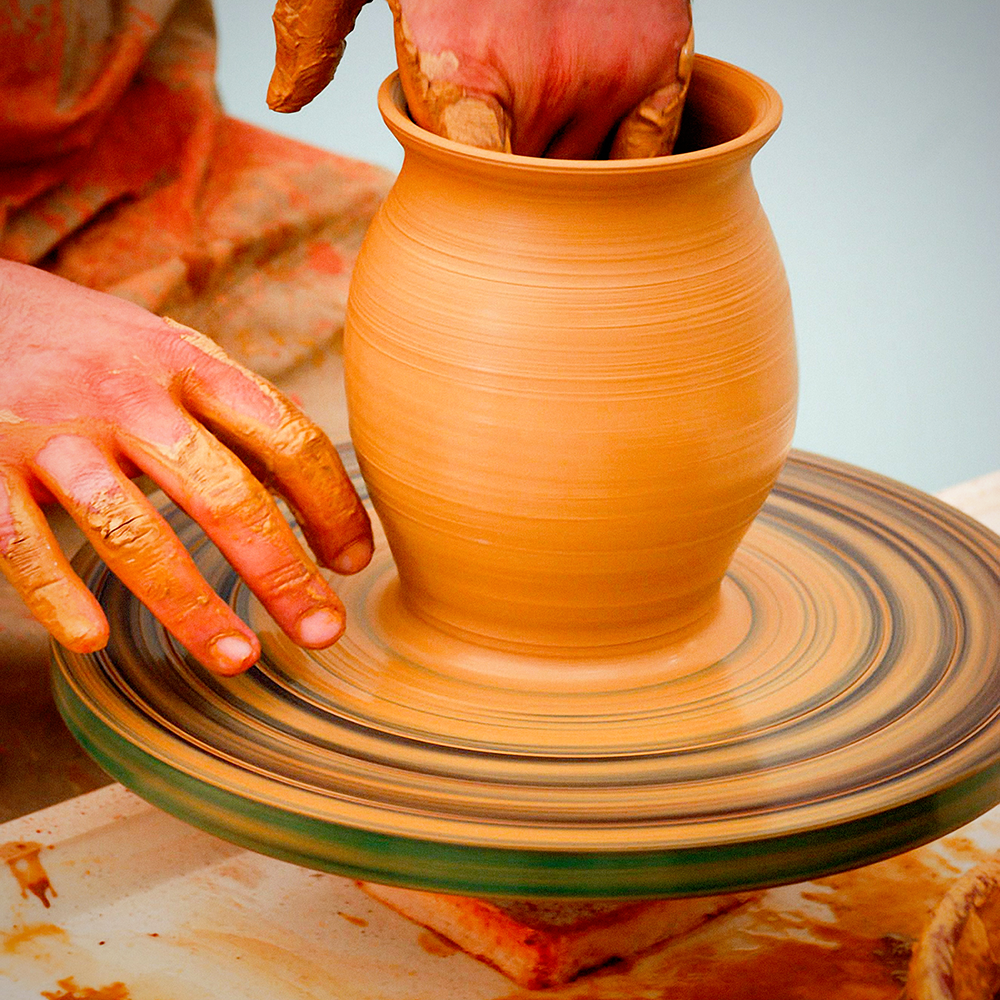



Techniques in Ceramic Arts by Ceramic Artists
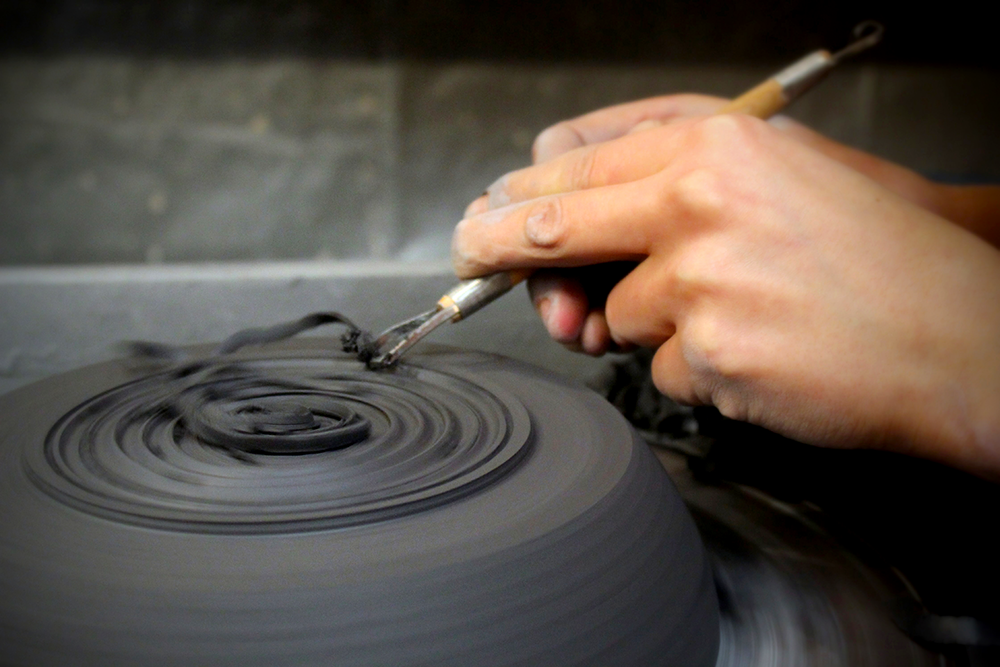
Ceramic techniques vary widely, from traditional methods like wheel throwing and slab construction to modern techniques like 3D printing.
Wheel throwing involves shaping clay on a rotating wheel, allowing potters to create symmetrical and intricate forms.
Slab construction involves rolling out clay into flat sheets and then cutting and assembling them into shapes.
Other techniques include hand-building, where clay is shaped using simple tools, and casting, where liquid clay is poured into molds.
Each technique offers unique possibilities for artistic expression, allowing ceramic artists to create a wide range of forms and textures.
The choice of technique often depends on the desired outcome and the properties of the clay being used.
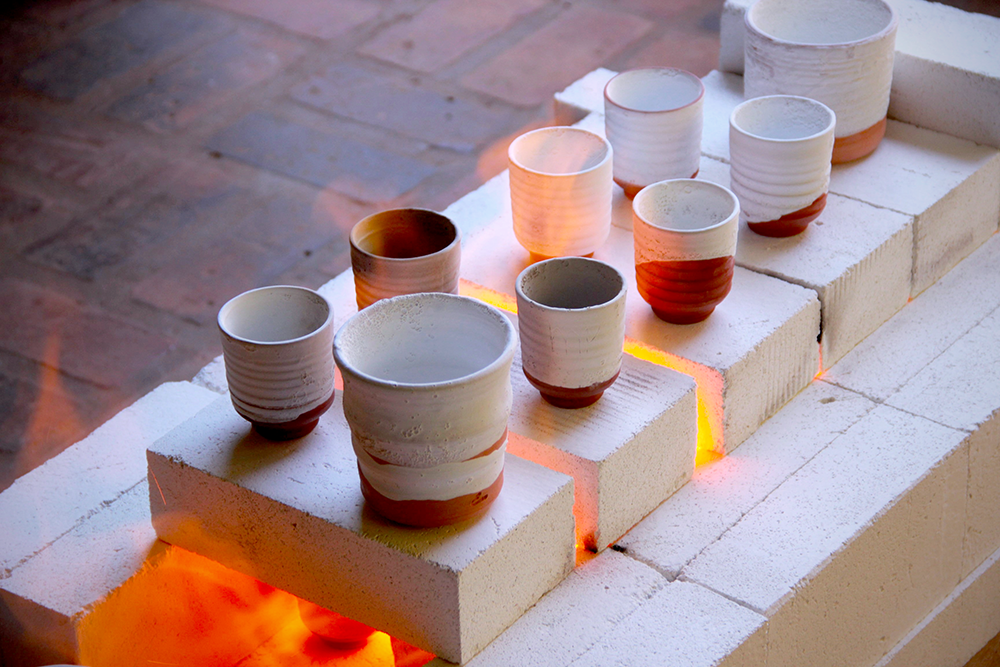
Firing Process in Ceramics
The firing process is a critical step in creating ceramic objects.
It involves heating the clay to high temperatures in a kiln, causing chemical changes that permanently harden the material.
During this process, clay particles fuse together to form a solid, glass-like surface.
The firing temperature and duration depend on the type of clay and the desired properties of the final product.
Bisque firing is the first stage, where the clay is heated to a lower temperature to remove moisture and organic materials.
This process makes the clay more durable and ready for glazing.
The second stage, known as glaze firing, involves applying a layer of glaze to the bisque-fired piece and then firing it again at a higher temperature.
The glaze melts and forms a glassy surface, adding color and texture to the ceramic object.
Applications of Ceramic Objects
Ceramics have a wide range of applications, from functional objects like dinnerware and cookware to decorative items like vases and sculptures.
Other ceramic materials, such as glaze, are also permanently changed when heated, similar to clay.
In addition to traditional ceramics, modern ceramics are used in various industries, including aerospace, electronics, and medicine.
Advanced ceramics are designed to withstand extreme conditions and are used in applications such as heat shields and medical implants.
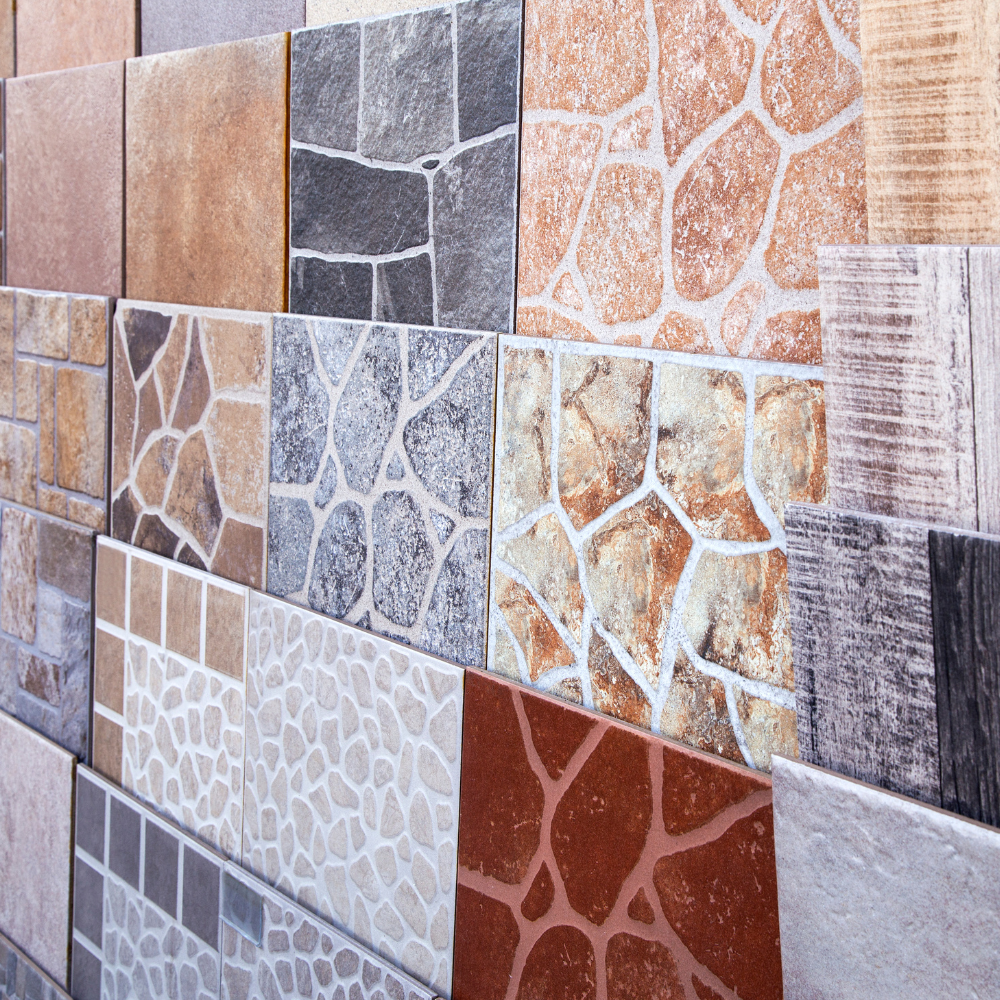
Ceramic tiles are commonly used for flooring and wall coverings, offering durability and aesthetic appeal.
Roof tiles made from ceramics provide weather resistance and longevity.
The versatility of ceramics makes them suitable for both artistic and practical purposes, allowing for endless possibilities in design and functionality.
Applications of Pottery
Pottery is primarily used for functional objects like bowls, plates, and vases.
These items are often created using a pottery wheel, which allows for precise shaping and symmetry.
Pottery can also be decorative, with intricate designs and glazes that add visual interest.
In addition to functional objects, pottery can be used for artistic expression.
Ceramic sculpture is a popular form of fine art, with artists creating intricate and detailed pieces that push the boundaries of traditional pottery.
Pottery items can also be used for practical purposes, such as flower pots and storage containers, combining functionality with aesthetic appeal.
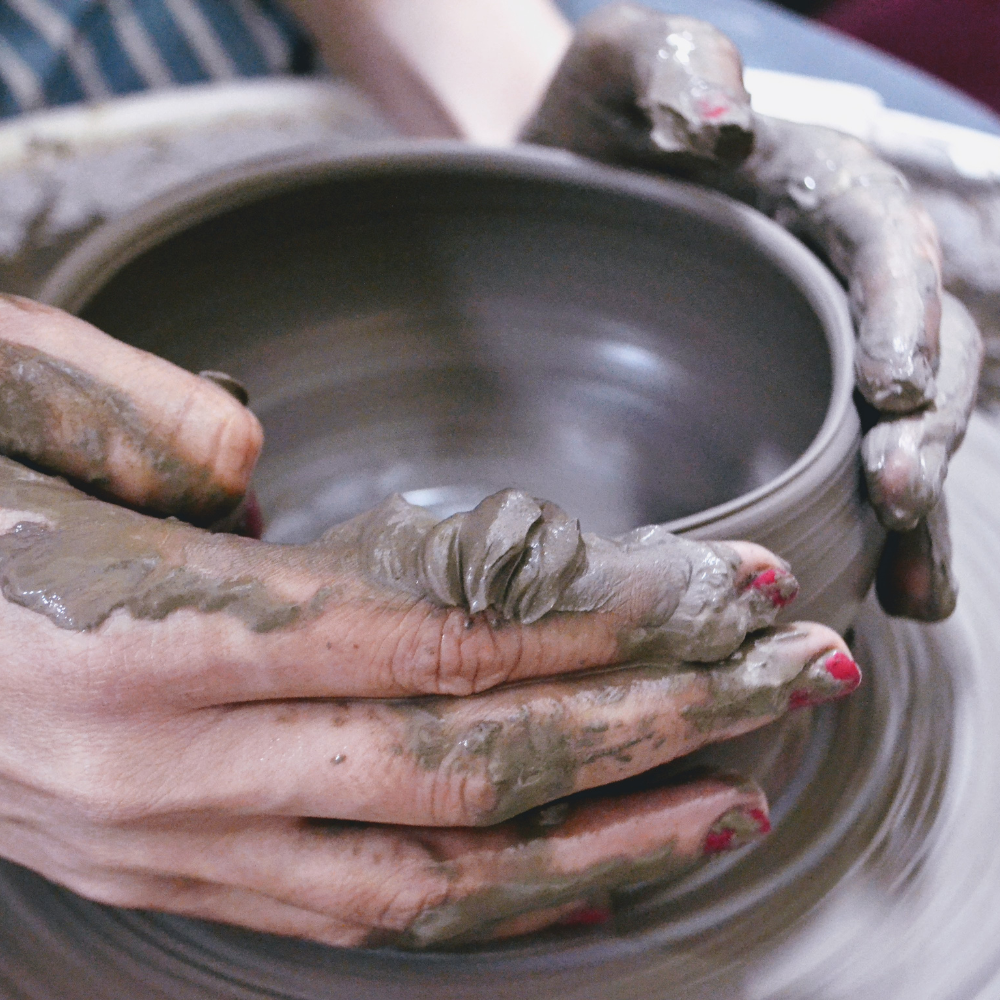
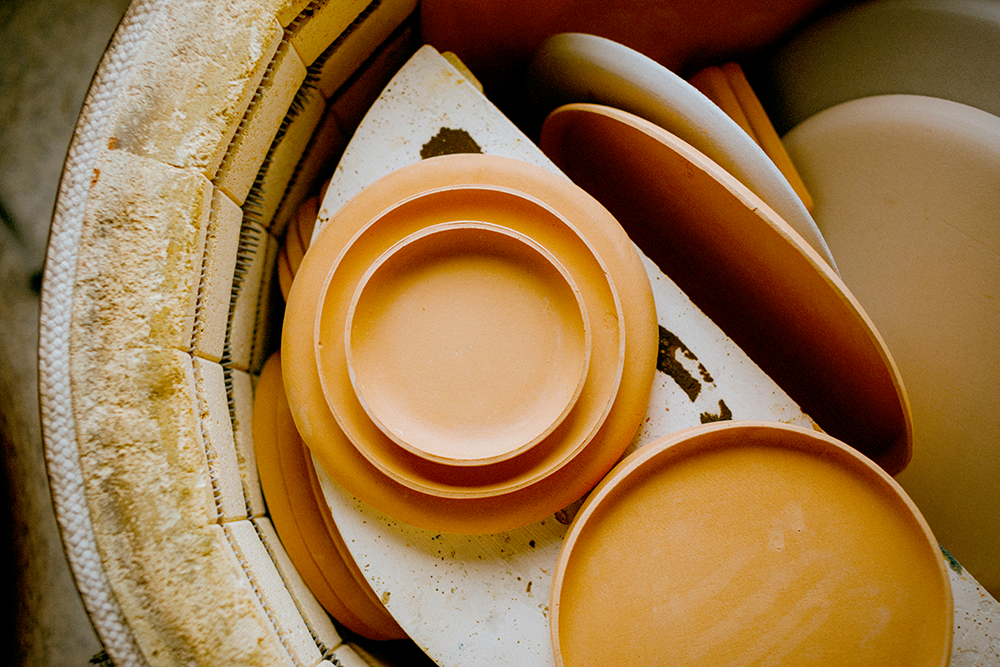
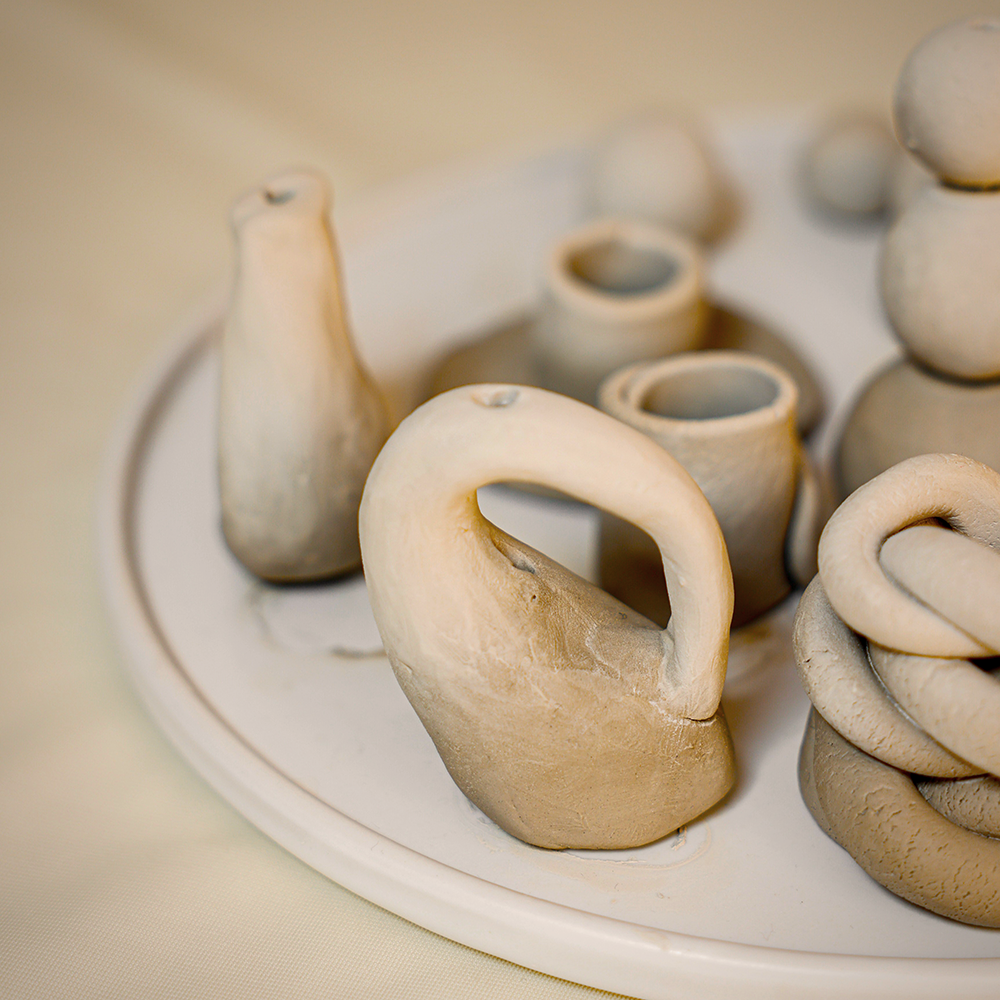



Differences in High Temperature Firing
One of the main differences between ceramics and pottery is the firing temperature.
Pottery typically uses lower temperatures for earthenware and higher temperatures for stoneware and porcelain.
Earthenware is fired at temperatures between 1,000 and 1,150 degrees Celsius, making it less durable and more porous.
Stoneware is fired at temperatures between 1,200 and 1,300 degrees Celsius, resulting in a non-porous and durable material.
Porcelain, known for its fine white color and translucency, is fired at even higher temperatures, between 1,300 and 1,450 degrees Celsius.
These high temperatures create a strong and durable material that is often used for fine china and other high-quality items.
The firing temperature affects the properties of the final product, making it essential for potters to choose the right temperature for their projects.
Differences in Materials
While pottery primarily uses clay, ceramics can include a variety of non-metallic materials.
In addition to clay, ceramics can be made from glass, metals, and other substances.
These materials are often combined with clay to enhance its properties and create unique textures and finishes.
For example, feldspar minerals are commonly added to clay to increase its strength and durability.
Iron oxide is used to create rich colors and patterns in ceramic glazes.
The choice of materials depends on the desired properties of the final product, allowing ceramic artists to experiment with different combinations and techniques.
Differences in Techniques
The techniques used in ceramics and pottery can vary widely, from traditional methods like wheel throwing and hand-building to modern techniques like 3D printing.
Pottery often relies on simple pottery tools and techniques, such as shaping clay on a pottery wheel or using molds to create uniform shapes.
Ceramics, on the other hand, can involve more complex processes, such as casting and glazing.
Advanced ceramics may require specialized equipment and techniques, such as high-temperature kilns and precision molding.
The choice of technique depends on the desired outcome and the properties of the materials being used, allowing for a wide range of possibilities in design and functionality.
Differences in Applications
While both ceramics and pottery can be used for functional and decorative purposes, their applications can differ significantly.
Pottery is often used for everyday items like bowls, plates, and vases, combining functionality with aesthetic appeal.
These items are typically created using traditional techniques and materials, such as earthenware and stoneware clay.
Ceramics, on the other hand, can be used for a wide range of applications, from fine art and decorative objects to industrial components and advanced materials.
Ceramic tiles are commonly used for flooring and wall coverings, offering durability and aesthetic appeal.
Advanced ceramics are used in various industries, including aerospace, electronics, and medicine, providing specialized properties and performance.
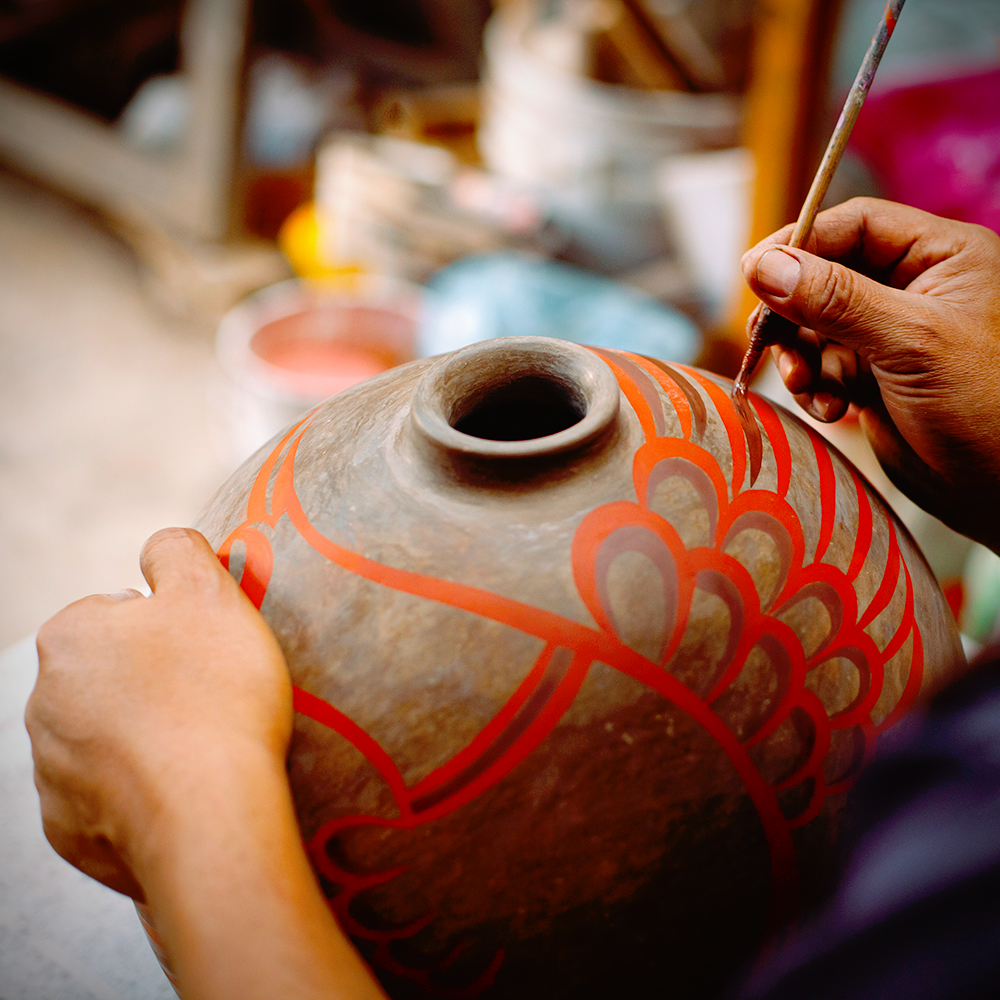



Differences in Artistic Expression
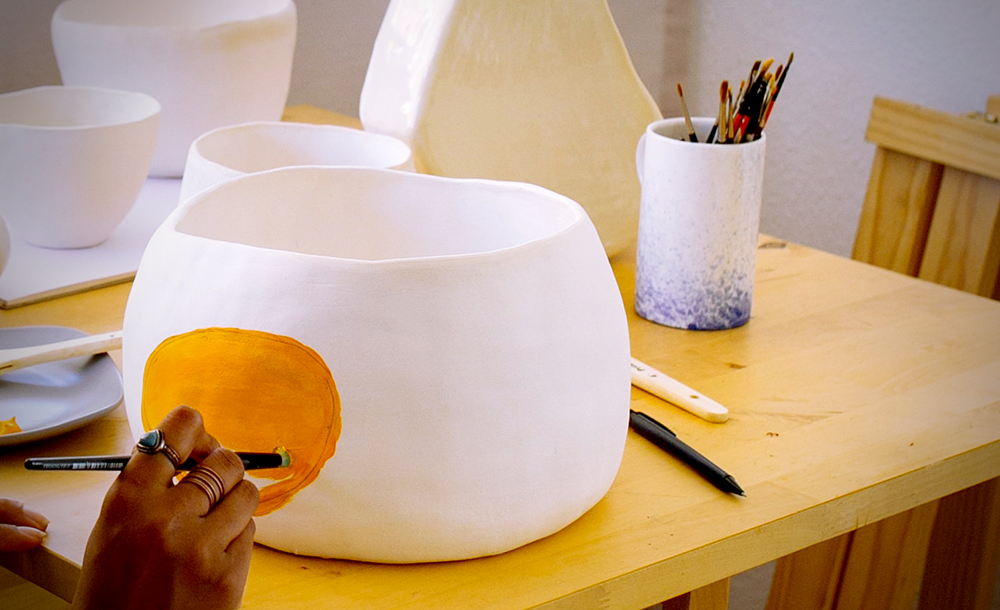
Both ceramics and pottery offer unique possibilities for artistic expression, allowing artists to create a wide range of forms and textures.
Pottery often focuses on functional objects, with intricate designs and glazes that add visual interest.
Ceramic sculpture is a popular form of fine art, with artists creating detailed and intricate pieces that push the boundaries of traditional pottery.
Ceramics, on the other hand, can involve more complex processes and materials, allowing for a wider range of artistic possibilities.
Advanced ceramics may require specialized equipment and techniques, such as high-temperature kilns and precision molding.
The choice of materials and techniques depends on the desired outcome, allowing ceramic artists to experiment with different combinations and create unique and innovative pieces.
Differences in Durability
The durability of ceramics and pottery depends on the materials and firing temperatures used.
Pottery made from earthenware clay is less durable and more porous than stoneware or porcelain.
Stoneware and porcelain, fired at higher temperatures, are more durable and non-porous, making them suitable for functional objects like dinnerware and cookware.
Ceramics, on the other hand, can include a wide range of materials with varying degrees of durability.
Advanced ceramics are designed to withstand extreme conditions and are used in applications such as heat shields and medical implants.
The choice of materials and firing temperatures affects the properties of the final product, making it essential for ceramic artists to choose the right combination for their projects.
Differences in Functionality
While both ceramics and pottery can be used for functional purposes, their functionality can differ significantly.
Pottery is often used for everyday items like bowls, plates, and vases, combining functionality with aesthetic appeal.
These items are typically created using traditional techniques and materials, such as earthenware and stoneware clay.
Ceramics, on the other hand, can be used for a wide range of functional purposes, from fine art and decorative objects to industrial components and advanced materials.
Ceramic tiles are commonly used for flooring and wall coverings, offering durability and aesthetic appeal.
Advanced ceramics are used in various industries, including aerospace, electronics, and medicine, providing specialized properties and performance.
Differences in Aesthetic Appeal
Both ceramics and pottery offer unique possibilities for aesthetic appeal, allowing artists to create a wide range of forms and textures.
Pottery often focuses on functional objects, with intricate designs and glazes that add visual interest.
Ceramic sculpture is a popular form of fine art, with artists creating detailed and intricate pieces that push the boundaries of traditional pottery.
Ceramics, on the other hand, can involve more complex processes and materials, allowing for a wider range of aesthetic possibilities.
Advanced ceramics may require specialized equipment and techniques, such as high-temperature kilns and precision molding.
The choice of materials and techniques depends on the desired outcome, allowing ceramic artists to experiment with different combinations and create unique and innovative pieces.



Differences in Historical Significance
Pottery has a long history, dating back thousands of years.
It is one of the oldest human crafts, with ancient civilizations using pottery for functional and decorative purposes.
Pottery artifacts provide valuable insights into the daily lives and cultures of ancient peoples, making it an important field of study for archaeologists and historians.
Ceramics, on the other hand, have a broader historical significance, encompassing a wide range of materials and techniques.
The development of ceramics has been influenced by advances in technology and materials science, leading to the creation of advanced ceramics used in modern industries.
The history of ceramics reflects the evolution of human ingenuity and creativity, making it a fascinating subject for study and exploration.
Differences in Cultural Significance
Pottery holds significant cultural importance in many societies, with traditional techniques and designs passed down through generations.
Pottery is often used in rituals and ceremonies, with specific forms and decorations holding symbolic meanings.
The cultural significance of pottery is reflected in the rich diversity of styles and techniques found around the world.
Ceramics, on the other hand, have a broader cultural significance, encompassing a wide range of materials and techniques.
The development of ceramics has been influenced by advances in technology and materials science, leading to the creation of advanced ceramics used in modern industries.
The cultural significance of ceramics reflects the evolution of human ingenuity and creativity, making it a fascinating subject for study and exploration.
Differences in Educational Opportunities
Both ceramics and pottery offer unique educational opportunities, allowing students to explore a wide range of materials and techniques.
Pottery classes often focus on traditional techniques like throwing pottery and hand-building, providing hands-on experience with clay and glazes.
These classes offer valuable insights into the history and cultural significance of pottery, as well as practical skills for creating functional and decorative objects.
Ceramics programs, on the other hand, may include a broader range of materials and techniques, from traditional methods to advanced processes like 3D printing and precision molding.
These programs often include coursework in materials science and engineering, providing a deeper understanding of the properties and applications of ceramics.
The choice of educational opportunities depends on the student's interests and career goals, allowing for a wide range of possibilities in the field of ceramic arts.
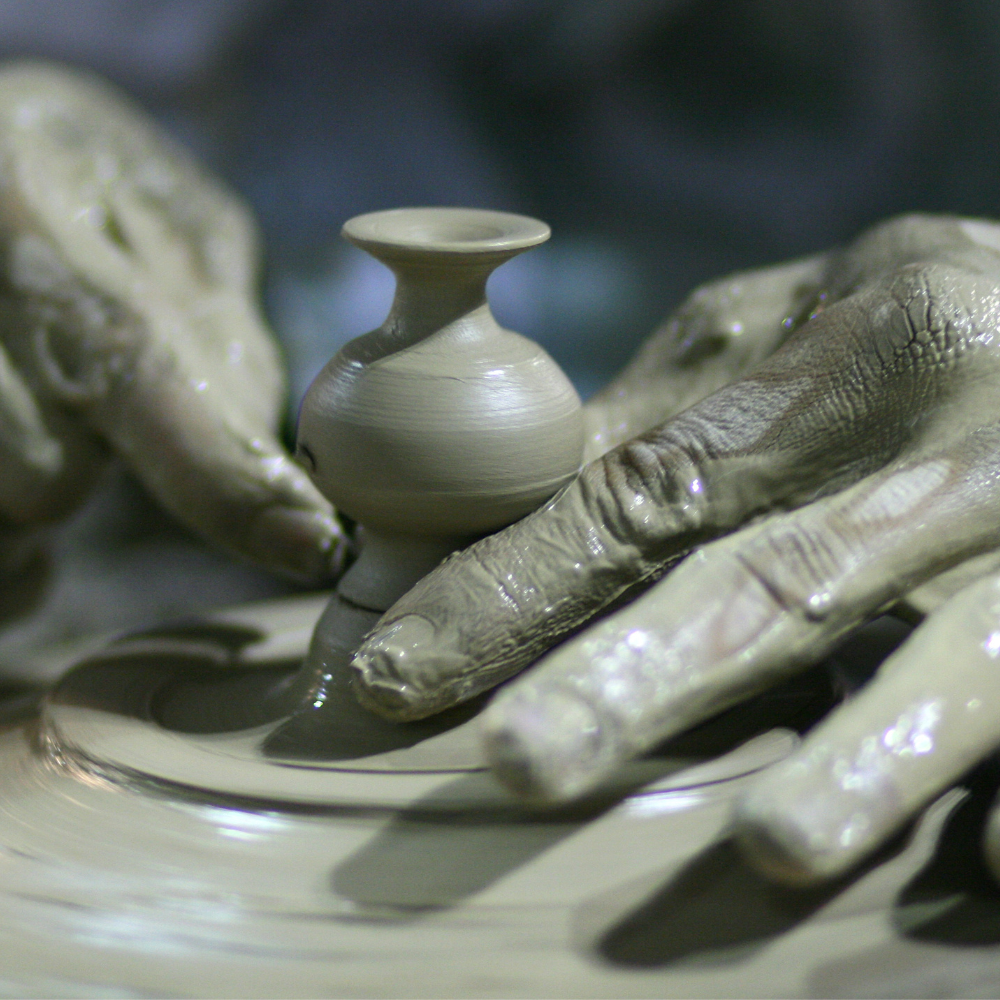



Embracing Ceramics and Pottery
In the mesmerizing realm of ceramic arts, distinguishing between ceramics and pottery is more than just a matter of terminology—it's a gateway to deeper appreciation and creativity.
By understanding the unique materials, techniques, and applications of each, you unlock endless possibilities for artistic expression and functional design.
While these terms are often used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings and applications.
Ceramics encompass a broad range of materials and techniques, while pottery specifically refers to items made from clay and fired at high temperatures.
The choice of materials, techniques, and firing temperatures affects the properties and functionality of the final product, allowing for endless possibilities in design and artistic expression.
So, whether you're a seasoned artist or a curious enthusiast, let this knowledge inspire you to explore, create, and celebrate the timeless beauty of ceramics and pottery.



Ceramics FAQs
Are you curious about the fascinating world of ceramics and pottery?
Whether you're a seasoned artisan or a budding enthusiast, this FAQ section is here to answer all your burning questions.
From understanding the core differences between ceramics and pottery to exploring the various types of clay and techniques used, we've got you covered.
Dive in to uncover the secrets behind these timeless crafts and elevate your knowledge to new heights!
What is the main difference between ceramics and pottery?
The main difference between ceramics and pottery lies in their scope and materials. Ceramics encompass a broad range of non-metallic materials that are permanently changed when heated, including clay, glass, and advanced materials. Pottery specifically refers to items made from clay and fired at high temperatures, such as bowls, plates, and vases.
What types of clay are used in pottery?
Pottery primarily uses three types of clay: earthenware, stoneware, and porcelain. Earthenware clay is a low fire clay that is porous and less durable. Stoneware clay is fired at higher temperatures, making it non-porous and more durable. Porcelain clay, known for its fine white color and translucency, is used to create fine china and other high-quality items.
What are some common techniques used in ceramics and pottery?
Common techniques used in ceramics and pottery include wheel throwing, slab construction, hand-building, and casting. Wheel throwing involves shaping clay on a rotating wheel, while slab construction involves rolling out clay into flat sheets and assembling them into shapes. Hand-building uses simple tools to shape clay, and casting involves pouring liquid clay into molds. Each technique offers unique possibilities for artistic expression and functionality.
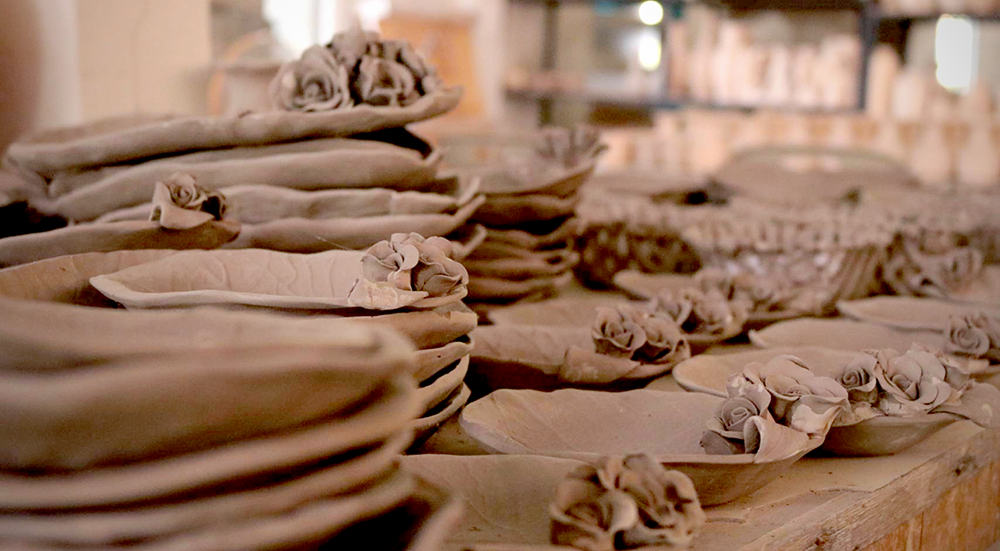
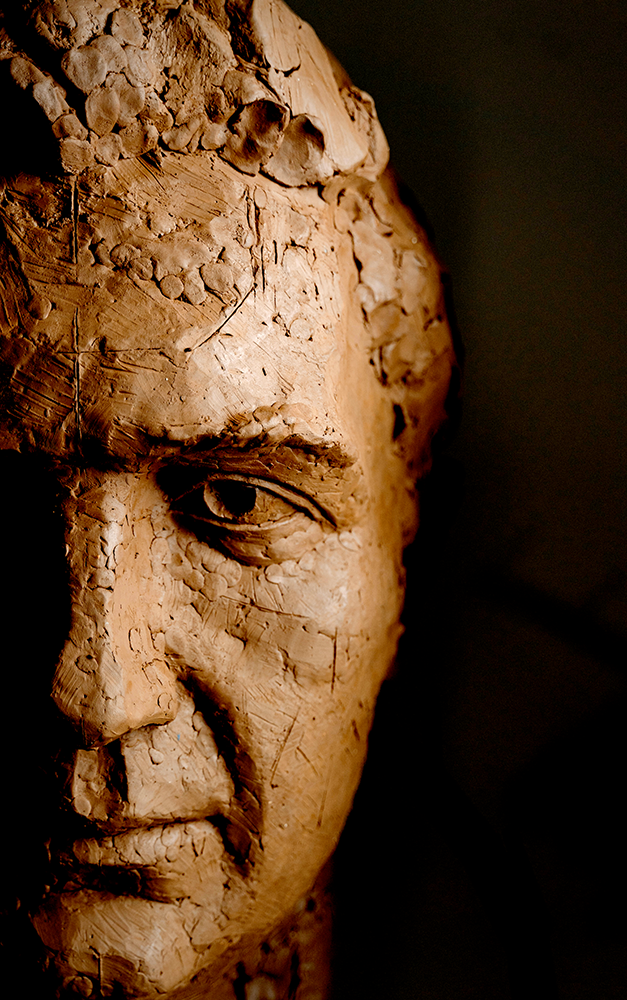



Eager to get your hands dirty and start creating? Check out Pottery to the People's video!
Want even more content about creativity and art?
Be sure to check out all of our creative chronicles!
Love pottery and working with clay?
Check out some of our other ceramic articles:
-What are the 5 methods of working with clay?
-What is the difference between hand building and throwing clay?










