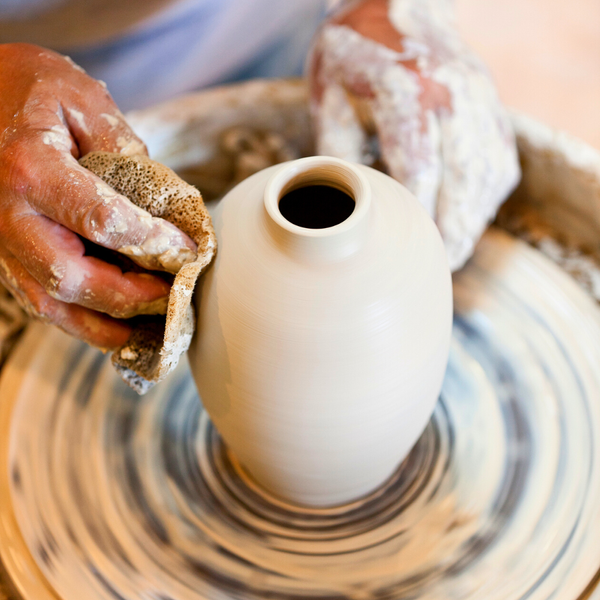
Clay: the ancient, pliable earth that has been the silent partner to human expression for millennia.
It's a material that whispers of the potter's wheel and ancient kilns, where the four elements of earth, water, air, and fire converge to birth artistry.
Today, the legacy continues as artists and hobbyists shape dreams and utility from this humble material.
In this exploratory journey, we will unleash the secrets of the five fundamental methods of working with clay.
Prepare your senses to get muddied with creativity and your spirit to be fired up, as we mold our understanding of this timeless craft!
Whether you're rolling up your sleeves for the first time or seeking to refine your mastery, the world of clay is vast and rewarding.
Let's spin the wheel, guide our hands and unearth the quintessential techniques that transform simple earth into extraordinary art!
Key Takeaways
- Hand building techniques such as the pinching method, coil construction, and slab technique permit the creation of varied clay forms from basic vessels to complex sculptures using simple tools and the artist’s hands.
- Wheel throwing requires a high level of skill to masterfully center, shape, and pull clay into symmetrical pieces, using tools like sponges and ribs to refine and finish the forms on a potter’s wheel.
- Alternative methods like extrusion and press molding offer efficient ways to create uniform, texturally diverse, and intricately patterned ceramics, suitable for both artistic expression and mass production.
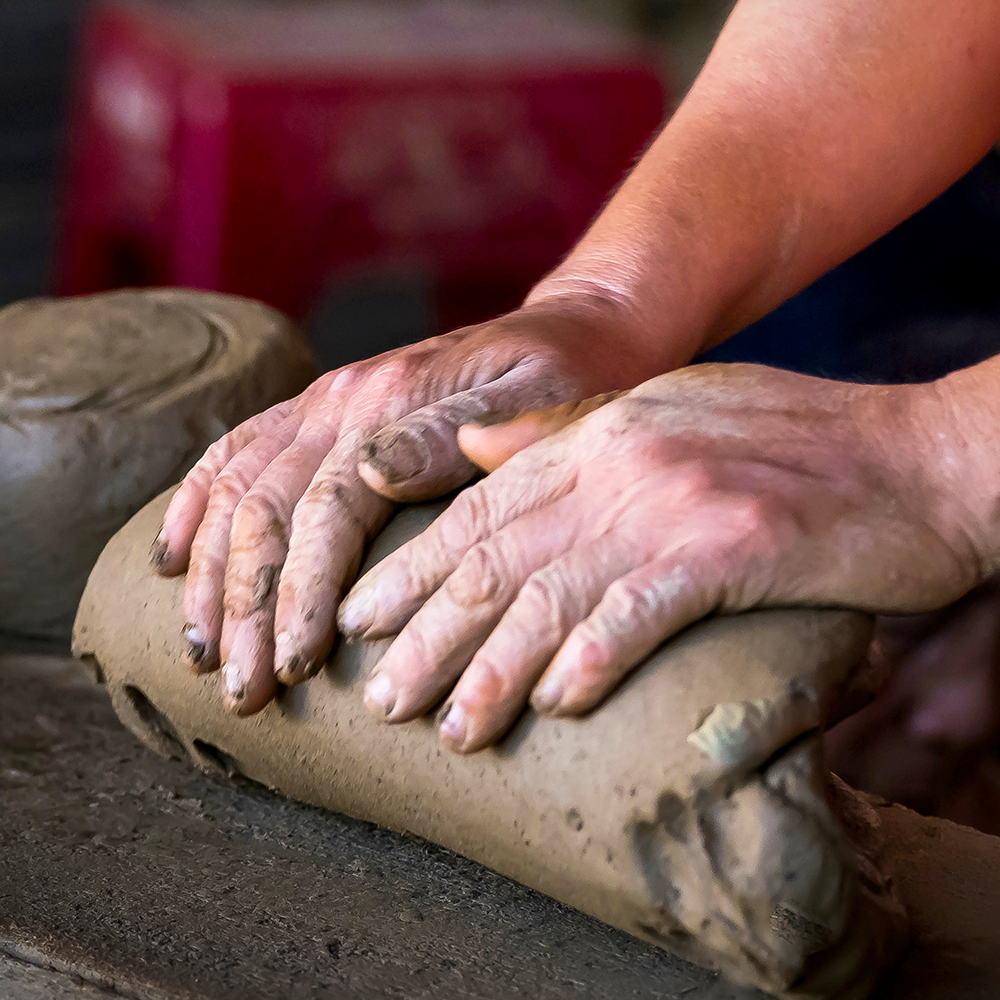



Exploring the Fundamentals of Handbuilding
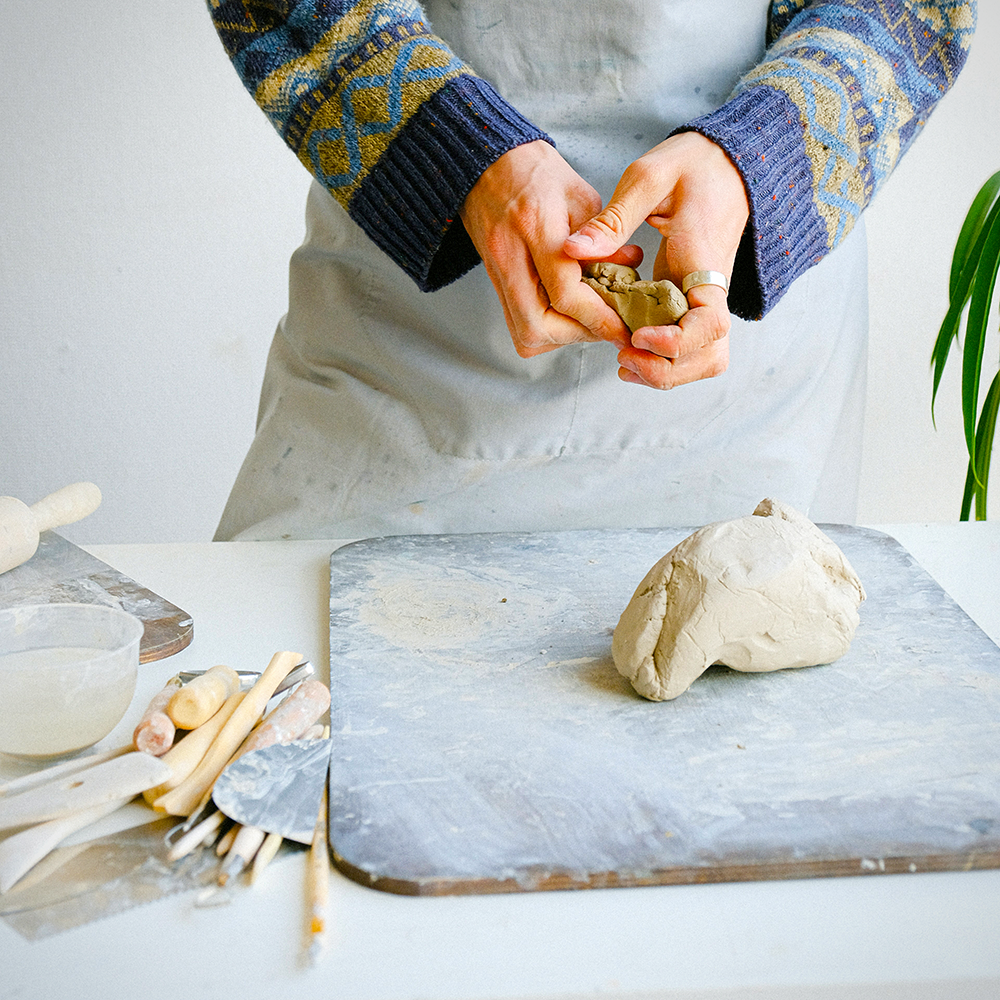
Clay hand building is an elemental technique that harks back to our earliest ancestors.
It offers a unique blend of simplicity and complexity, allowing the creation of various forms using only clay and the human hand.
From the primal pinch pot method to the artful coil construction and slab technique, each method holds its unique charm and potential for creativity.
By exploring various clay hand building techniques, artists can unlock endless possibilities in their work.
Regardless of your experience level, the journey of clay hand building continually presents new aspects to discover and perfect.
Pinching Method: Creating Forms from the Palm of Your Hand
The beauty of the pinching method lies in its simplicity.
It starts with a ball of clay, and with your thumb pressed into the center, the clay is shaped by a pinching motion using your fingers.
This technique opens up a world of possibilities, allowing artists to create a range of shapes and sizes, from small pinch pots to intricate sculptures.
Yet, achieving the best results with the pinching method isn’t solely about improvisation - a keen eye for detail is crucial.
Uniform wall thickness is key to preventing warping or cracking during firing.
For beginners, starting with a ball of wet clay about the size of a small orange or smaller can be a good learning ground, as it transitions into soft clay when manipulated.
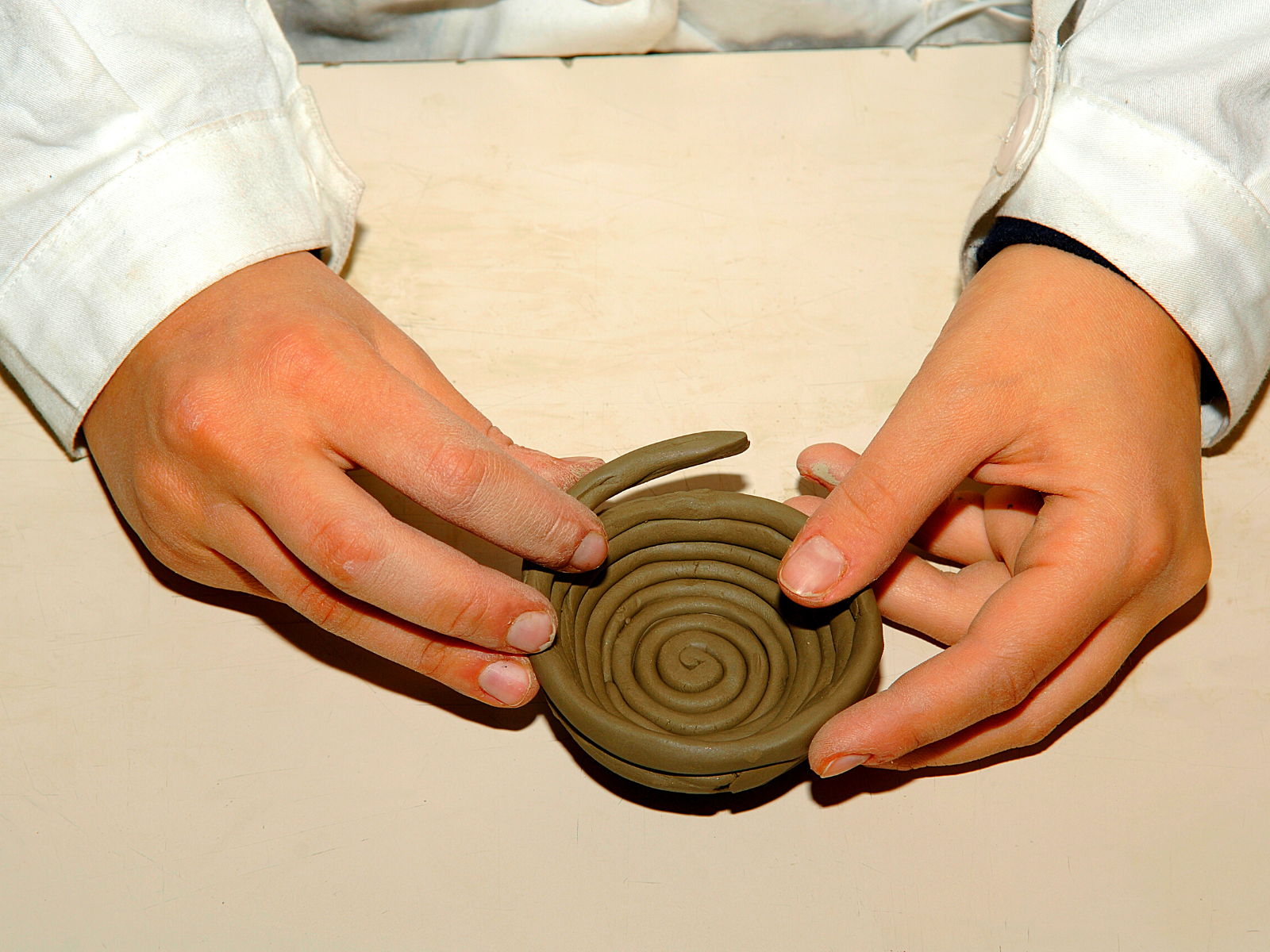
Coil Construction: The Art of Rolling and Stacking
Stepping up from the pinching method, coil construction offers a pathway to larger ceramic forms.
This technique involves rolling out thick strips of clay, then stacking and joining them to form the walls of pots or larger items.
The coils used in construction can vary in size, usually between the diameter of a penny and that of a nickel, and maintaining the correct moisture level is crucial to avoid cracking.
A slip and score method is utilized for effective joining of these coils.
This process uses a slip mixture to bond coils together, ensuring a secure and strengthened structure.
And to prevent weak spots, coils are cut diagonally and joined with staggered joints, an essential technique for the stability of larger vessels.
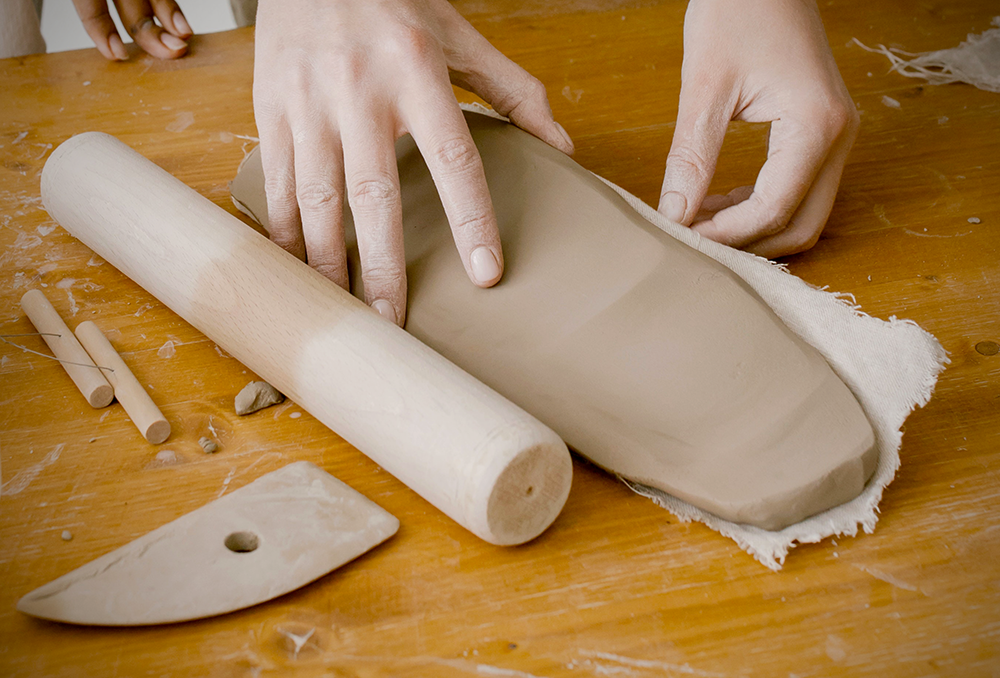
Slab Technique: Crafting with Flat Pieces of Clay
The slab technique, unlike the previous methods, involves crafting with flat pieces of clay.
It’s a method that offers a diverse range of possibilities, from simple cups and bowls to complex clay sculptures and geometrical forms.
With nothing more than a slab roller or rolling pin to flatten the clay, a fettling knife and wire cutters for precise cuts, and scoring tools for joining the slabs together, you can bring your designs to life.
Slab construction, also known as slab building, is a process that is both systematic and liberating. Here are the steps involved in soft slab construction:
- Start with a design sketch.
- Prepare the clay by wedging it.
- Roll the clay into slabs, creating a clay slab.
- Cut the slabs into the desired shape.
- Allow the slabs to reach a leather-hard stage.
- Undergo a slow drying process with airflow.
With this technique, even beginners can create a variety of clay projects, including planters and dishes, without needing a pottery wheel.



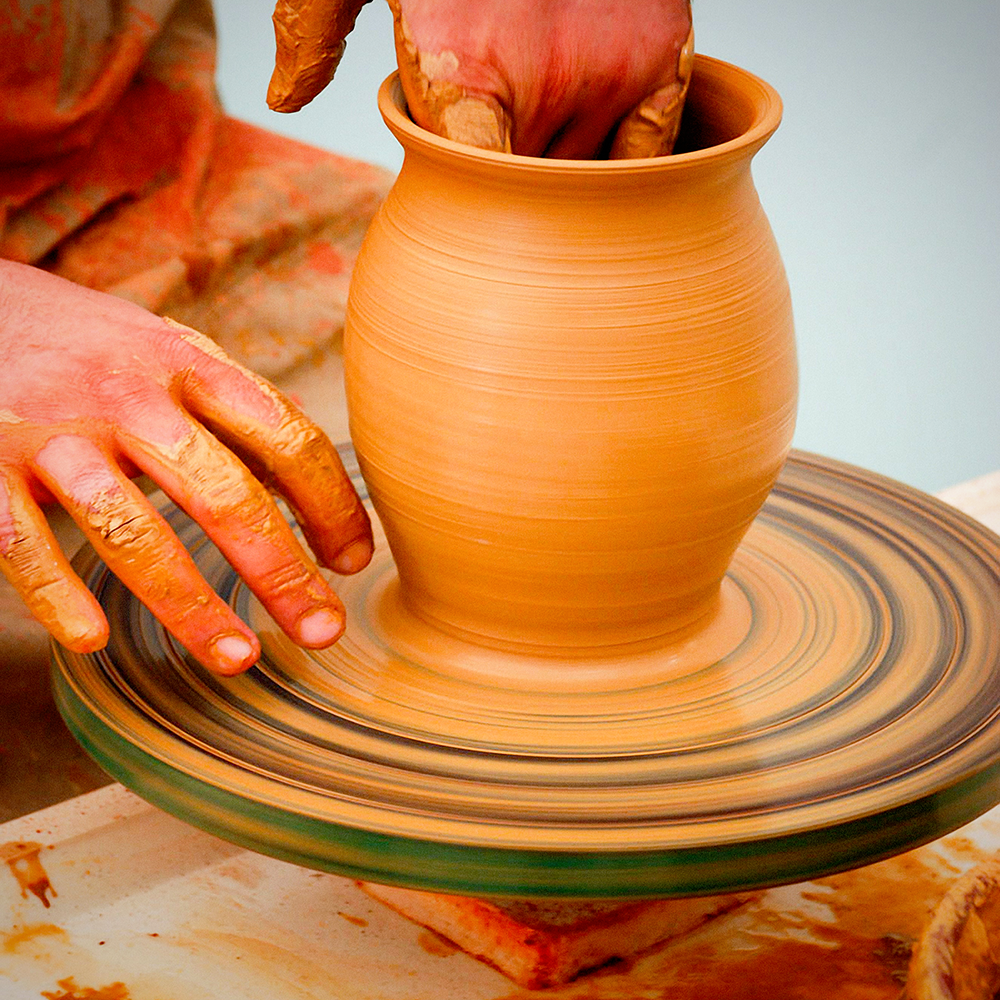
Potter's Wheel: Throwing Clay into Shape
While hand building offers a primal connection with clay, mastering the potter’s wheel opens up another dimension of pottery making.
This process involves creating symmetrical, round objects such as bowls, plates, and vases on a potter’s wheel.
It’s a dance of hands and clay, a delicate balance between control and surrender, where the slightest shift can alter the entire form.
Each step in the pottery crafting process, from wedging and centering the clay on the wheel head to opening, pulling, and shaping it into a cylinder, plays a vital role in creating pottery with smooth surfaces and uniform walls.
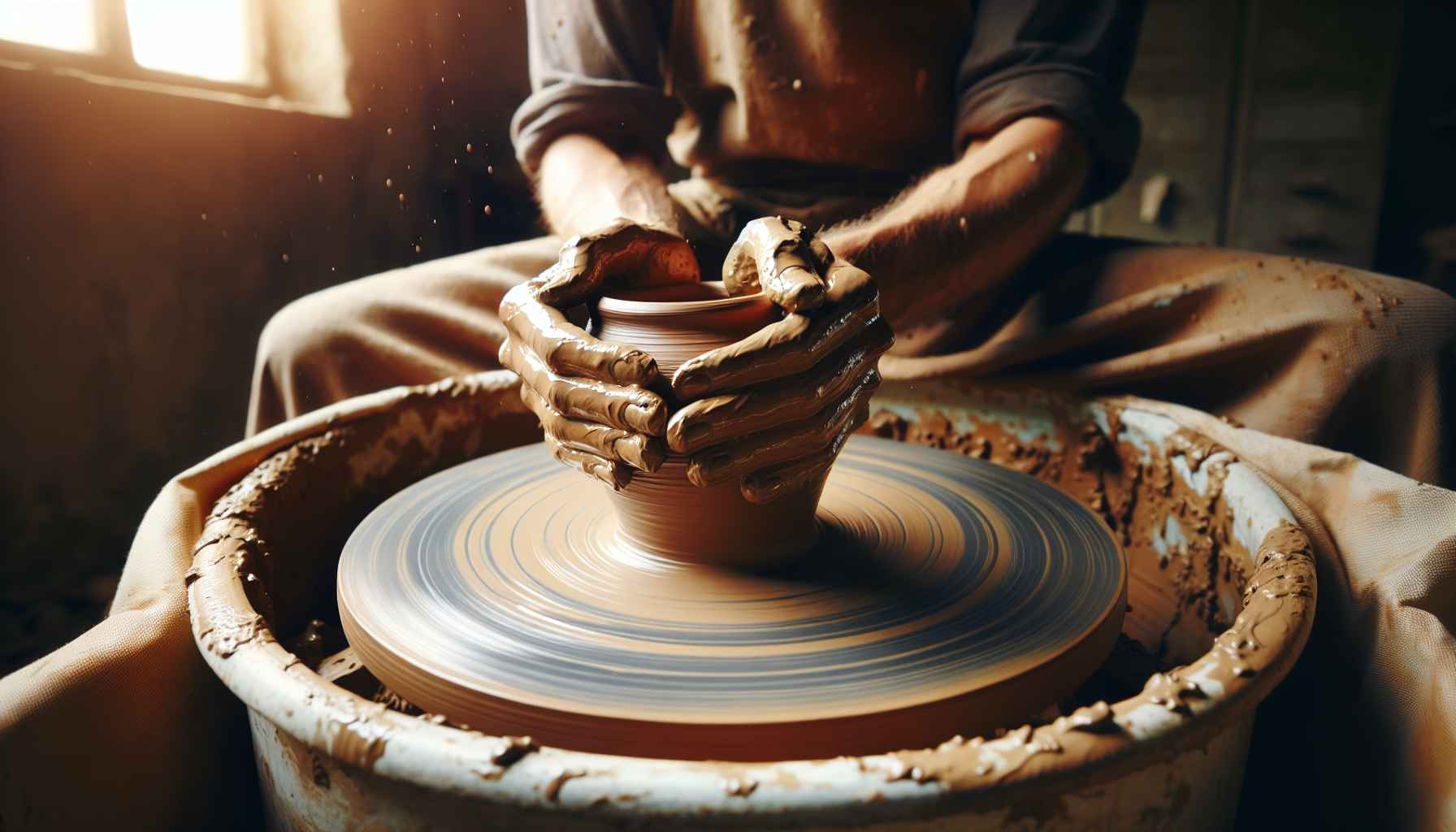
Centering and Shaping: The Heart of Wheel Throwing
In the art of wheel throwing, centering the clay on the potter’s wheel is the foundation of creating symmetrical pieces.
This critical step involves adjusting the wheel speed, applying consistent pressure, and keeping elbows anchored to maintain control while centering the clay.
Once the clay is centered, the shaping begins.
This is where the magic happens as you position your hands around the clay, constricting or expanding the clay’s walls.
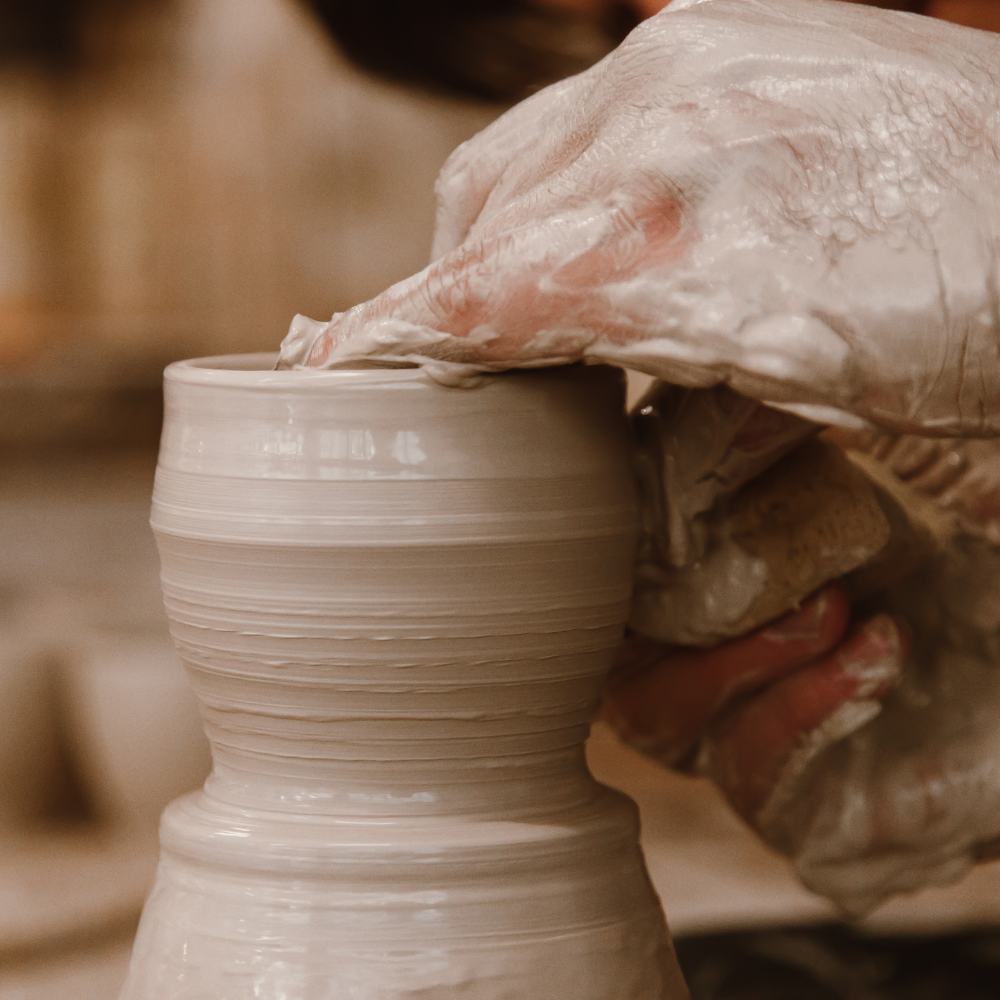
Skilled throwers use different parts of their hands, such as the palms, fingers, and knuckles, to refine the form.
Pulling up the walls of the vessel requires a steady and smooth upward motion coordinated between both hands.
And finally, pottery tools like sponges and ribs help in smoothing surfaces and achieving uniform thickness in the piece being thrown.



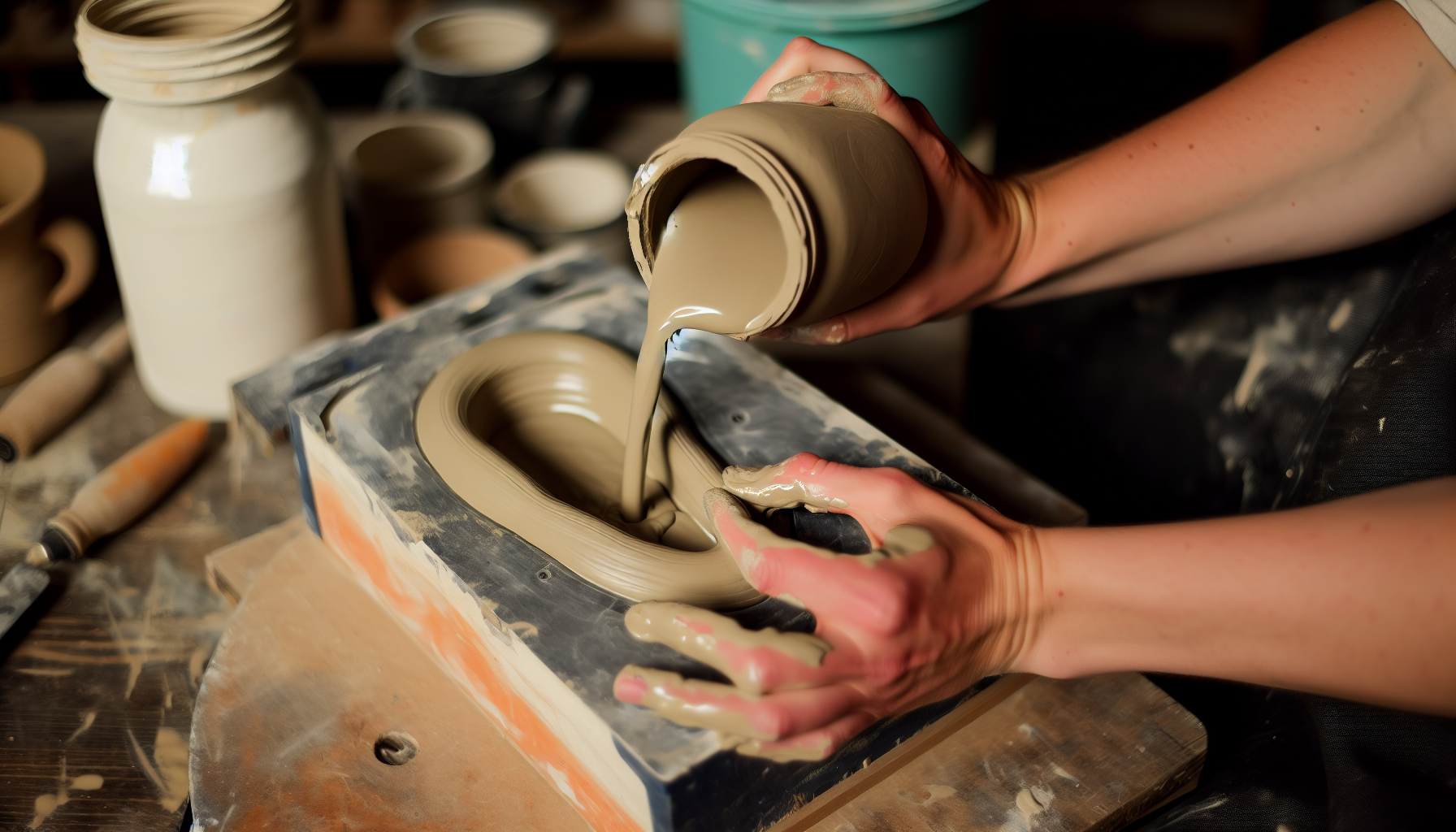
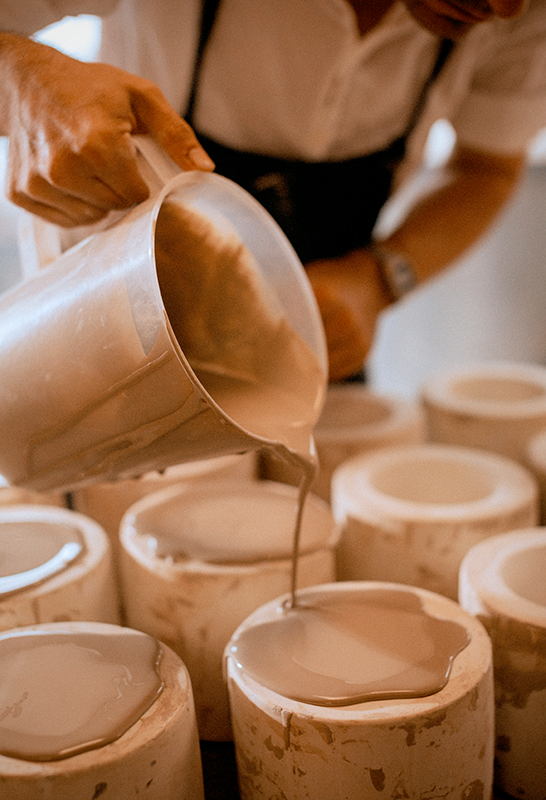
Slip Casting: Precision and Replication
As we move away from solid clay, we encounter an innovative technique known as slip casting.
This process involves:
- Pouring liquid clay into a plaster mold to create ceramic pieces
- Providing an intriguing twist to traditional clay crafting methods
- Offering precision and replication
- Being well-suited for mass production
- Enabling the creation of detailed shapes that might be challenging to make on a pottery wheel.
We’ll delve deeper to understand how this process functions.
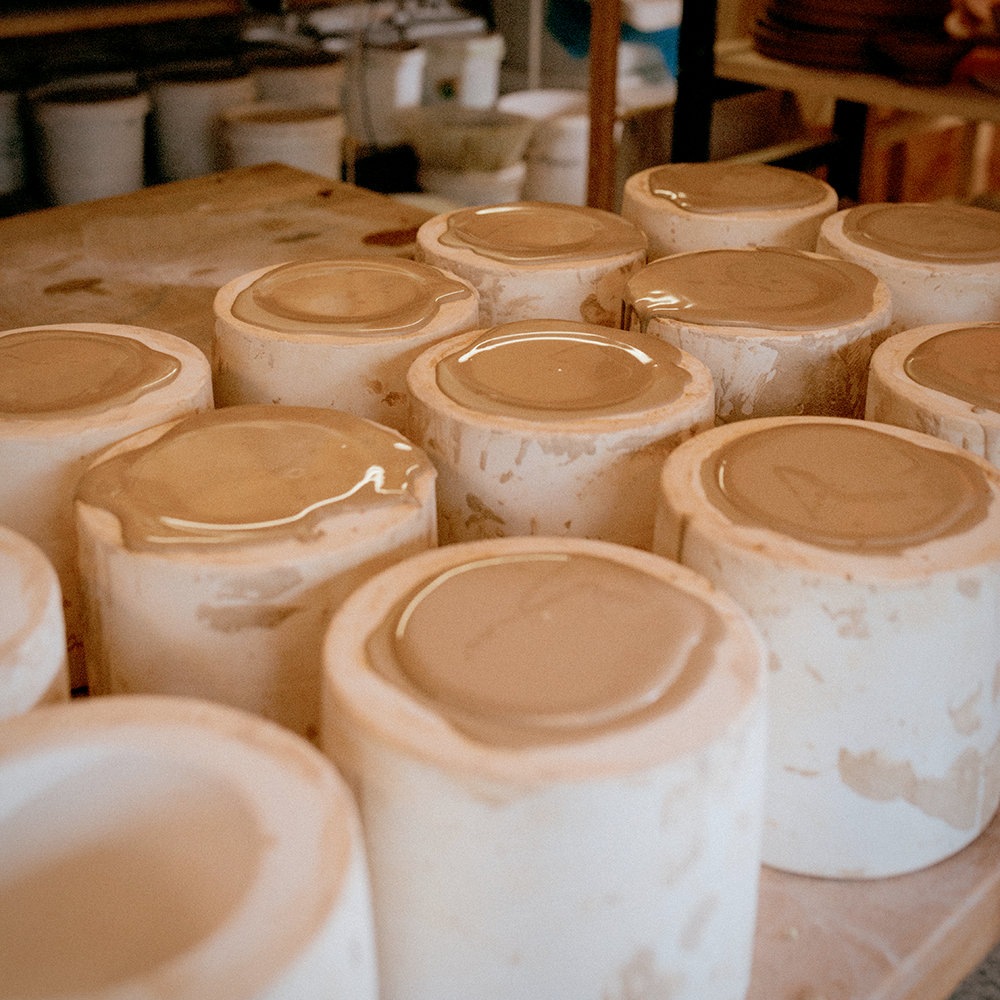
Plaster Mold Creation: Blueprint for Ceramic Pieces
The crux of slip casting lies in the creation of plaster molds.
It begins with a prototype design, the blueprint for your ceramic piece.
Selecting the right prototype material is of utmost importance as it directly affects the quality of the final mold.
Materials like blue foam can be used, with a smooth, well-detailed surface being essential for the fidelity of the final plaster mold.
As you construct your plaster mold, here are the steps to follow:
- Position cottle boards around the prototype before pouring the plaster.
- Add registration keys to ensure proper alignment.
- Apply a release agent, such as Murphy Oil Soap, to prevent sticking.
- Incorporate specific components, such as PVC piping, as a pour hole to facilitate consistency in the slip casting process.



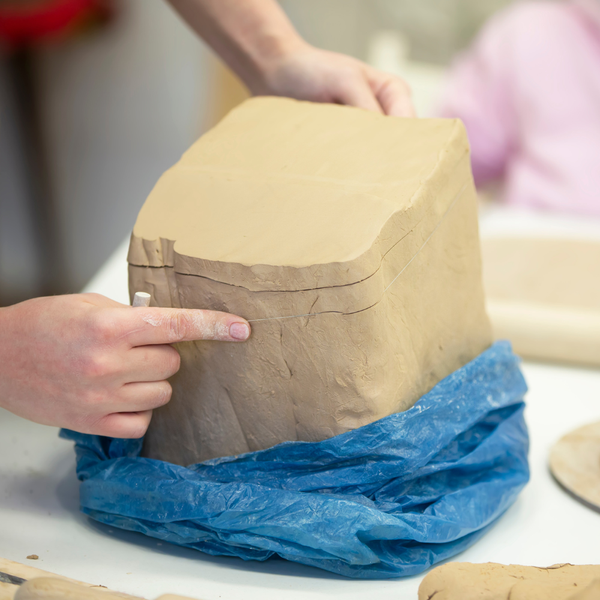
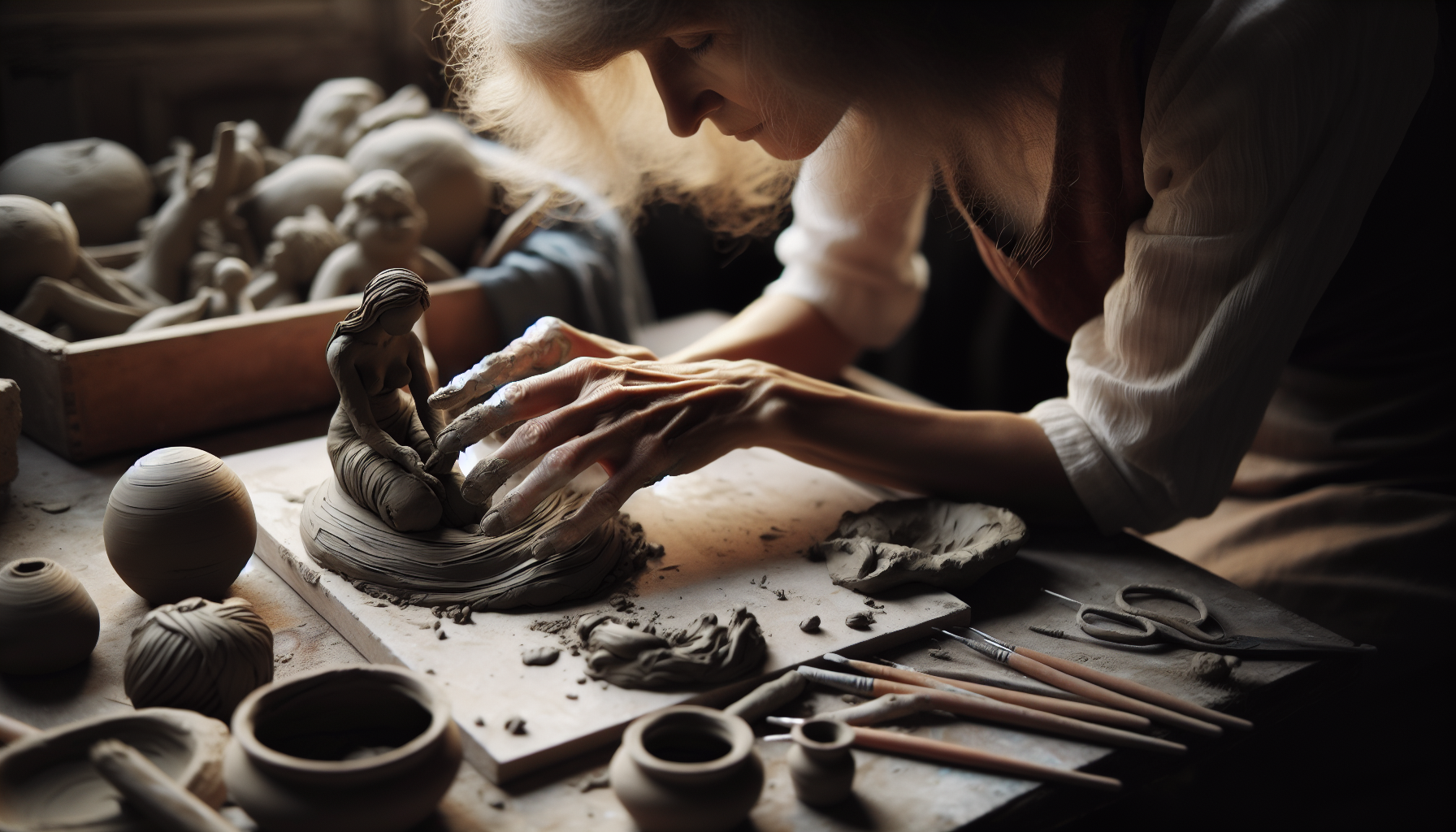
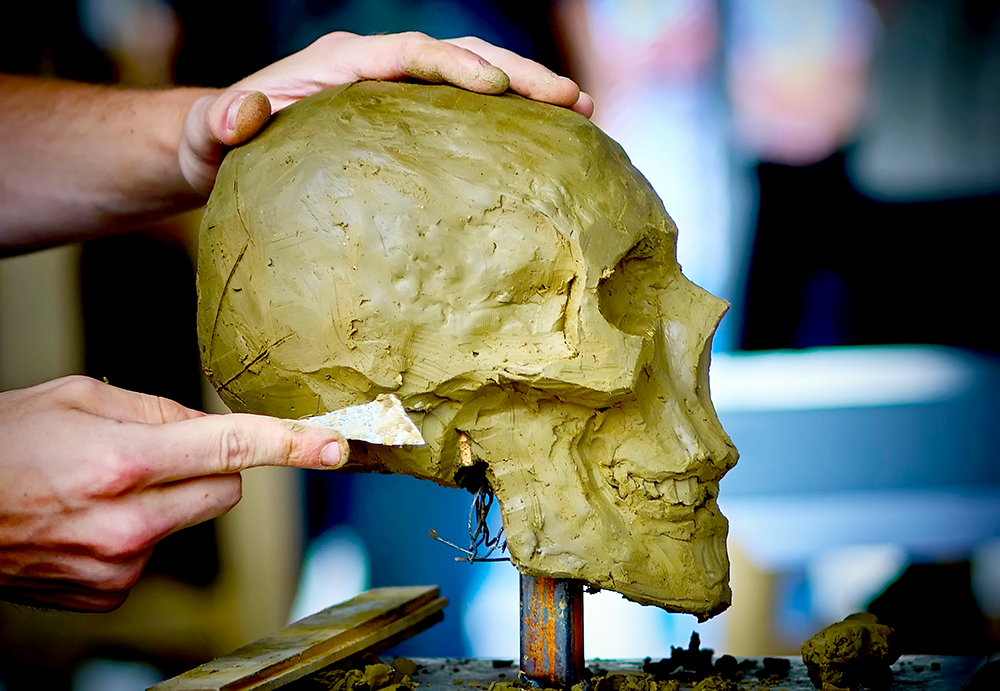
Sculpting Clay: Expressive Forms & Textures
Sculpting solid clay takes us into the realm of expressive forms and detailed textures.
This technique allows for the creation of:
- intricate, detailed, and realistic forms, such as figurines, busts, or relief sculptures
- an exploration of patience, practice, and a keen eye for proportions and form
- ideal for artists dedicated to crafting expressive pieces.
Mastering this form of ceramic arts requires a deep understanding of modeling tools.
Adding Dimension to Clay Forms: Modeling Tool Mastery
Modeling tools are the sculptor’s best friends.
They unlock the potential for high levels of detail in the artwork, enhancing expressiveness and adding intricate details to clay sculptures.
From hook tools for fine manipulations, scoring tools for adding textures like scaling or feathers, to wire loop tools for sculpting concave curvatures, each tool has its unique utility.
Then we have scrapers, or ribs, serving multifaceted purposes including texturing, cutting, smoothing, and even cleaning the artist’s workspace.
Sharp knives and clay sculpting knives also play a multifunctional role in cutting, texturing, and smoothing clay forms.
Even a pin tool can be instrumental in creating unique textures through cutting, piercing, and incising designs.
The mastery of these tools transforms clay into dynamic and intricate forms, adding both dimension and detail to sculptures.


Alternative Methods: Beyond the Basics
Delving deeper into the world of clay crafting reveals alternative forming methods, each with their own unique advantages.
Ceramic techniques like extrusion and press molding break away from the traditional methods, introducing new possibilities in the creation of uniform shapes, intricate profiles, and textured patterns in ceramics.
Extrusion: Uniform Shapes and Intricate Profiles
Extrusion stands at the intersection of artistry and efficiency.
This process involves an extruder, a tool equipped with a barrel and internal screw, used to push clay through a die or mold, giving it shape.
By changing the dies or molds, a variety of different shapes and profiles can be created from the same machine, offering immense versatility.
The use of extrusion is advantageous for ensuring uniform shapes and sizes, particularly critical for the production of building materials where standardization is key.
But it’s not just about uniformity.
Post-extrusion modifications can transform extruded clay pieces into a variety of structures, thus enhancing their versatility beyond creating uniform shapes.
Press Molding: Quick Forms with Texture and Pattern
Press molding is another alternative method that offers unique benefits.
This technique involves:
- forcing clay into a mold to assume a specific shape
- replicating the shape uniformly
- producing large quantities of ceramics such as bowls, plates, and tiles
It’s an efficient process that is often used in mass production.
There are two main types of press molds: plaster cast press molds, made with Plaster of Paris and talc, and bisque molds, created by shaping clay over forms and firing at a low temperature.
To create textures and patterns, the clay is rolled out to an even thickness, placed over the mold, and allowed to dry to leather-hard before being removed and fired.
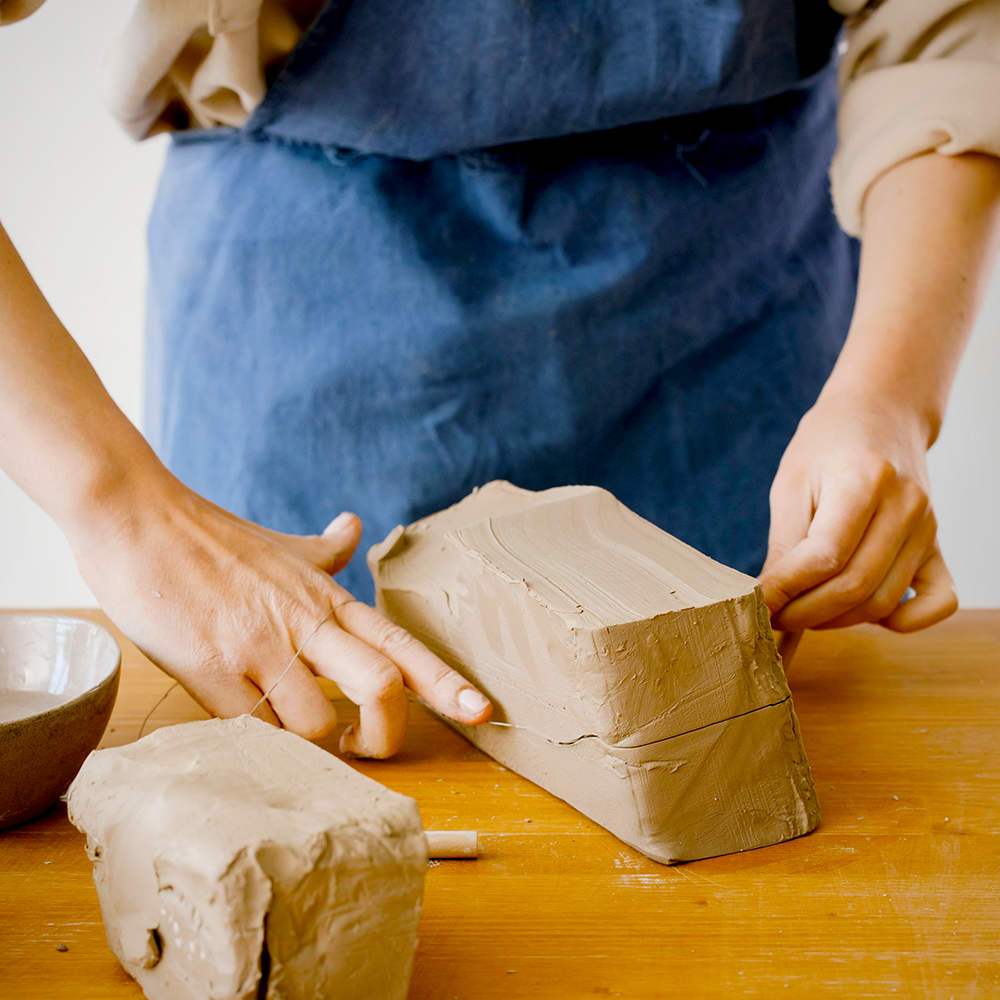
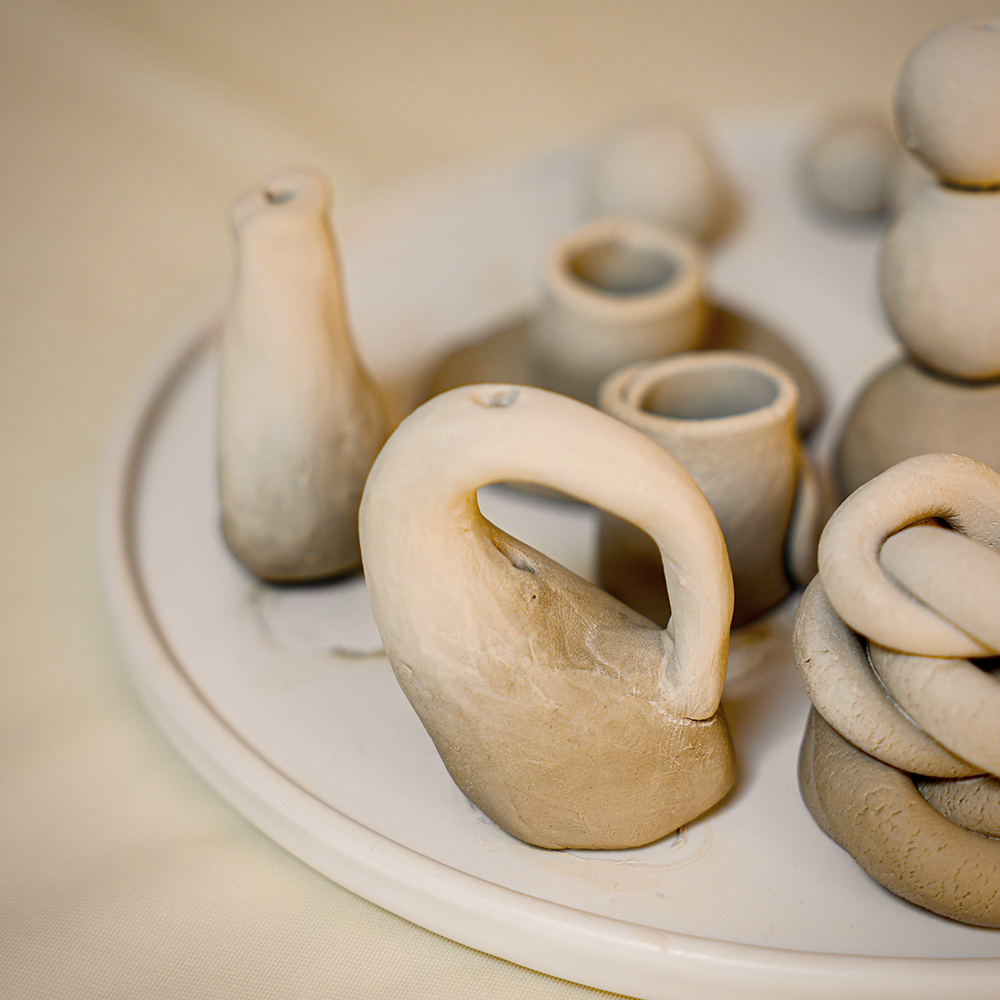



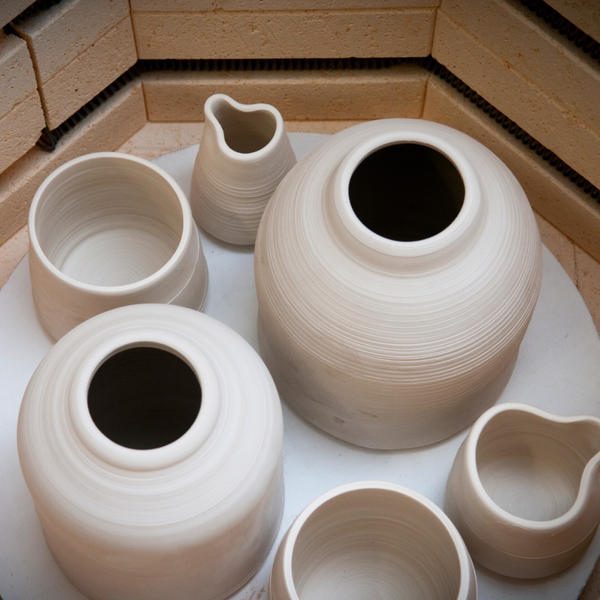
Clay Crafting is an Endless Journey
The fundamentals we’ve explored in this guide are just the beginning of your journey into clay crafting.
With every method, tool, and technique you learn, new possibilities emerge, offering limitless avenues for creativity.
From primal hand building methods to intricate sculpting techniques, each process holds its unique potential for expression and exploration.
From the fundamentals of hand building to mastering the potter’s wheel, exploring slip casting, sculpting solid clay, and unveiling alternative forming methods, we’ve journeyed through the enchanting world of clay crafting.
Each technique, with its unique nuances and potential, offers a distinct pathway to creativity.
As you venture into your own clay crafting journey, remember that the essence of this art lies not just in the final product, but in the transformative process of shaping clay into a reflection of your creativity.
So, pick up your tools, get your hands dirty, and let the journey into the world of clay begin!



Ceramics FAQs
If you're just getting started with ceramics, you may have some questions.
Here are a few commonly asked questions and their answers to help you along your clay crafting journey.
What are the 5 basic building techniques in clay?
The 5 basic building techniques in clay are forming clay, hand-building, slab building, coiling, and throwing pottery. You can also explore extruding and slip casting for more advanced ceramics projects.
What are the methods of clay work?
The most common methods of clay work are pinchpot, coiling, and slab techniques, which offer diverse artistic possibilities. Explore hand building to unleash the infinite artistic potential of this craft.
What is the significance of centering in wheel throwing?
Centering in pottery throwing is significant because it is essential for creating symmetrical pieces, which involves adjusting the wheel speed, applying consistent pressure, and maintaining control over the clay.
How does slip casting work?
Slip casting works by pouring liquid clay into a plaster mold to create ceramic pieces. This method is great for mass production and allows for the production of detailed shapes difficult to achieve on a pottery wheel.
What tools are essential for sculpting solid clay?
To sculpt solid clay, essential tools include hook tools, scoring tools, wire loop tools, scrapers or ribs, and sharp knives or clay sculpting knives for refining forms. These tools are crucial for fine manipulations, adding textures, sculpting curvatures, and smoothing.



Eager to get your hands dirty and start working with clay? Check out Andy Ward's Ancient Pottery's video!
Want even more content about creativity and art?
Be sure to check out all of our creative chronicles!
Love pottery and working with clay?
Check out some of our other ceramic articles:










