3D printing can be a great tool for artists.
It allows you to print three-dimensional objects, including prototypes, unique pieces of art, or even production pieces.
In this blog post, we will exploring the different ways that artists can use 3D printing.
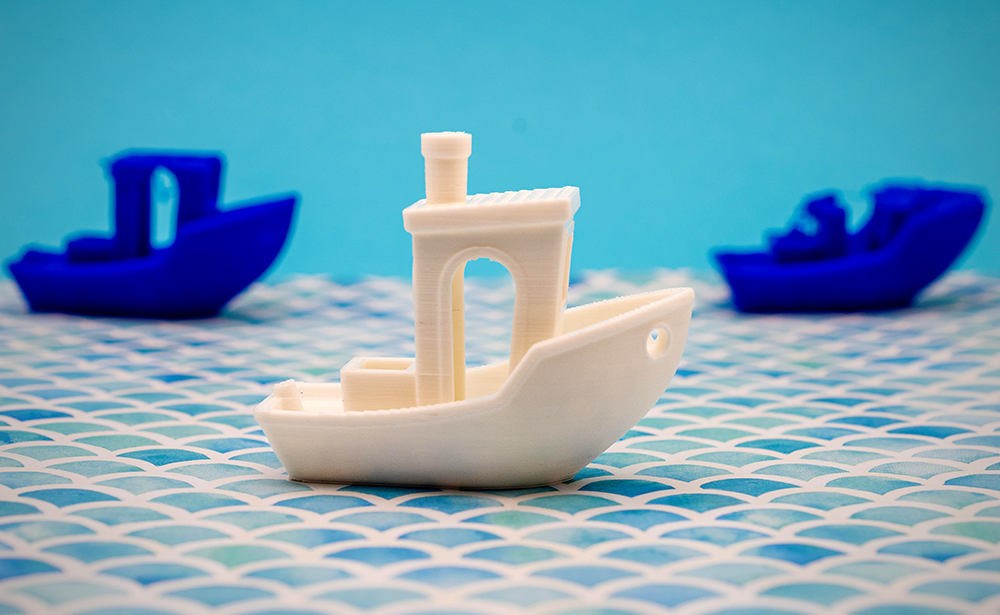



What Is 3D Printing?
3D printing is a process of making three-dimensional solid objects from a digital file.
The creation of a 3D printed object is achieved using additive manufacturing processes.
In a manufacturing process an object is created by laying down successive layers of material until the entire object is created.
Each of these layers can be seen as a thinly sliced horizontal cross-section of the eventual object.
3D printing is the opposite of subtractive manufacturing which involves taking away material by methods such as drilling or milling.
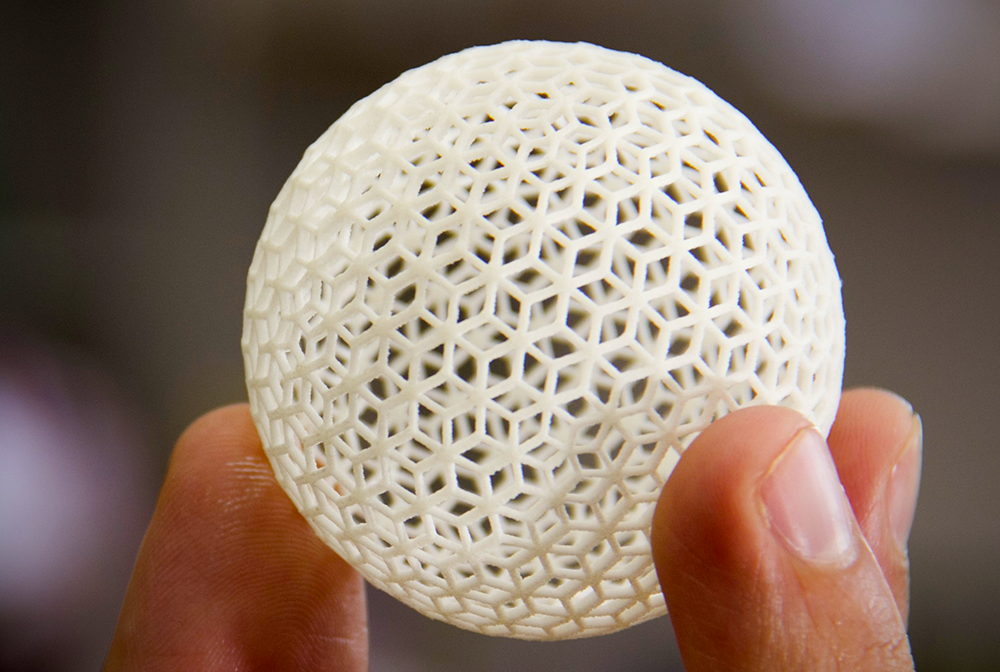
Additive manufacturing can be used to create complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to create using traditional manufacturing methods.
The ability to produce complex shapes has led to the use of 3D printing for both prototyping and mass production in many industries including architecture, automotive, aerospace, military, engineering, sporting goods, fashion and medicine.


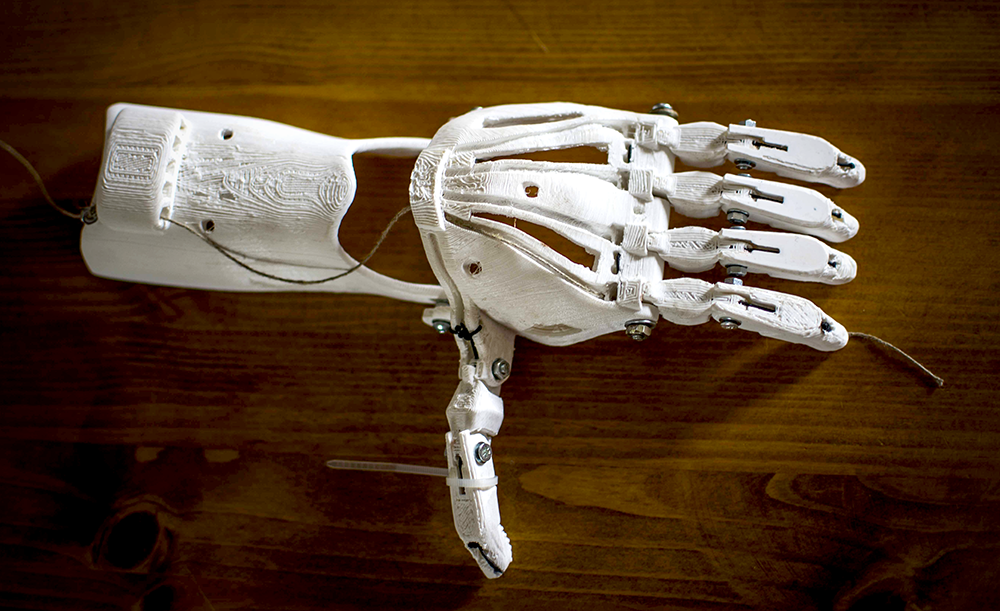
How 3D Printers Work
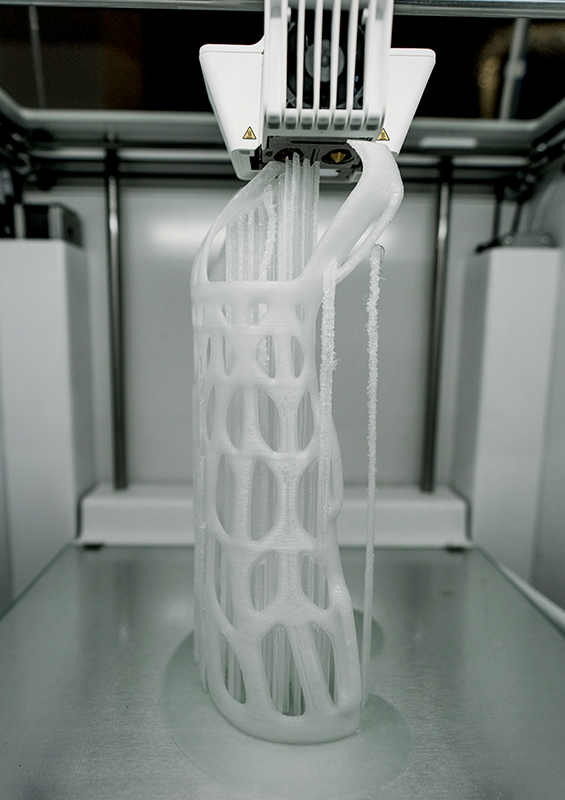
3D printers usually work by extruding thin layers of molten plastic or liquid resin, which quickly cools and solidifies as it hits the air.
The object is built up layer by layer from the bottom up.
The advantage of this type of additive manufacturing over subtractive manufacturing methods is that no material is wasted as the unwanted parts can be melted down and reused.
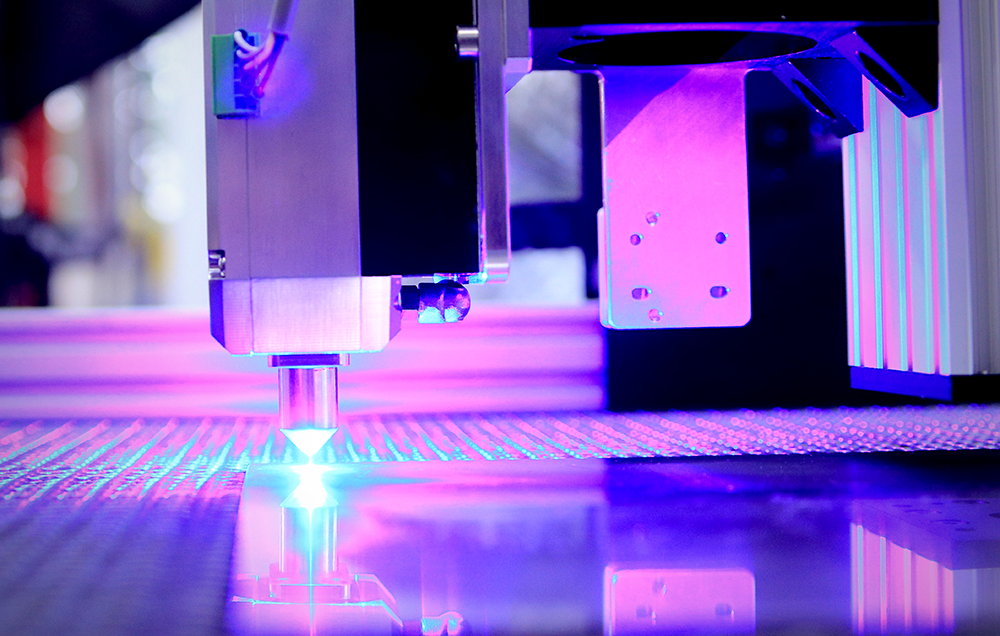
Another type of 3D printing technology called powder bed fusion works by selectively melting powder using a laser or an electron beam.
This method can be used with metals, plastics and ceramics to create very strong and detailed objects.
Stereolithography (SLA) is another popular type of 3D printing technology which uses ultraviolet lasers to cure polymer resins into solid objects.
SLA printers are generally quite expensive but produce high quality prints with smooth surfaces.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is similar to SLA but uses powdered metals or plastics instead of liquid resins.
SLS printers are also quite expensive but have the advantage that they can produce functional parts from strong materials such as nylon and titanium.
Direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) is a type of SLS that uses metals instead of plastics.
This technology can be used to create strong metal parts with very fine details.
Digital light processing (DLP) is another type of 3D printing technology which uses a projector to cure photopolymer resins.
This technology is similar to SLA but is generally faster and cheaper.
Material jetting is a type of 3D printing that works by depositing droplets of photopolymer resin onto a build platform.
The build platform is then exposed to UV light which cures the resin and creates the desired object.
This technology is similar to SLA but is generally faster and produces smoother surfaces.
Selective laser melting (SLM) and direct metal laser melting (DMLM) are two common powder bed fusion methods.
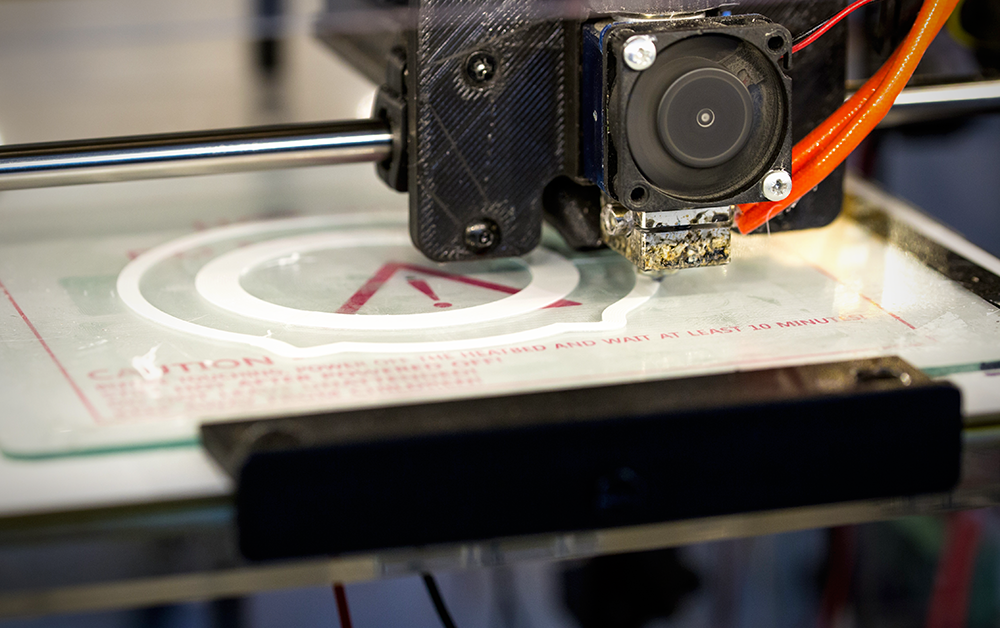
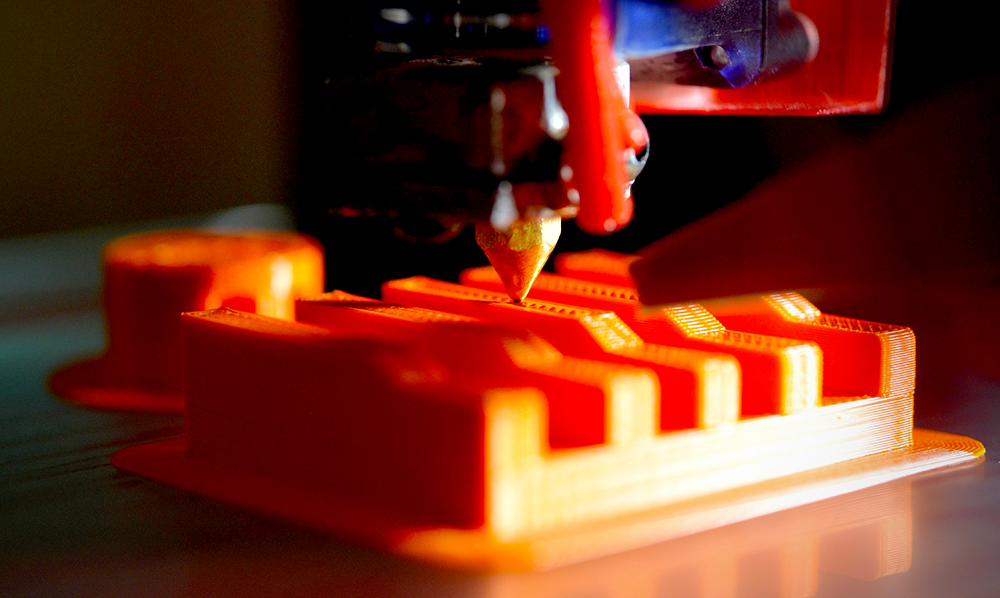


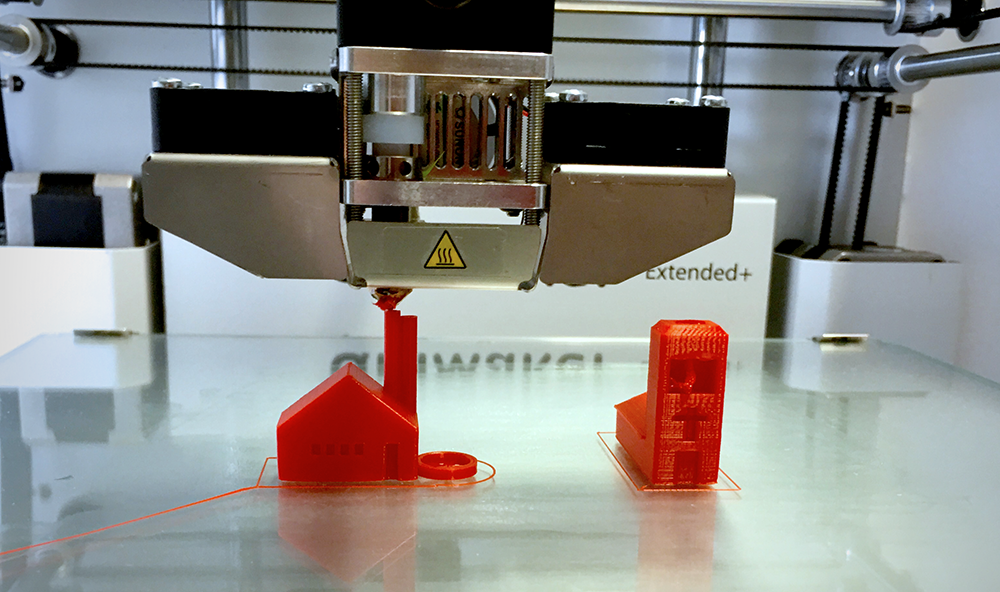
3D Printing Materials
3D printing can be used with multiple materials including metals, plastics, ceramics and even food.
The most common type of 3D printing filament is thermoplastic which can be made from a variety of different plastics such as ABS, PLA, PETG, nylon and polycarbonate.
Thermoplastic filaments are generally easy to use and produce strong prints with good detail.
They can also be easily sanded and painted to create a smooth finish.
Metal filaments are also available, using metal powder fused with a laser beam, but are generally much more expensive and difficult to use.
Ceramic filaments are also available but are not as common as thermoplastic or metal filaments.
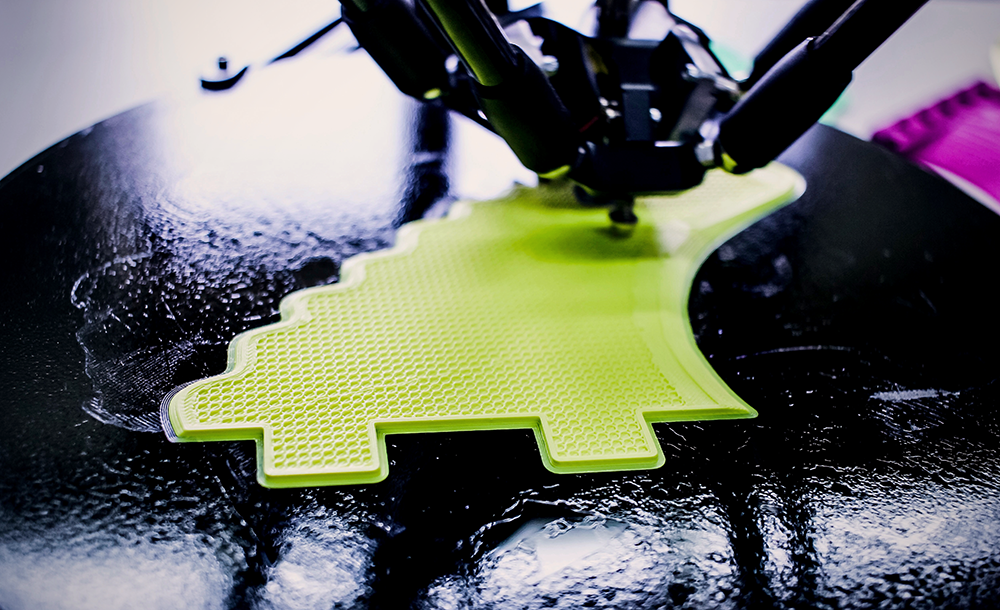
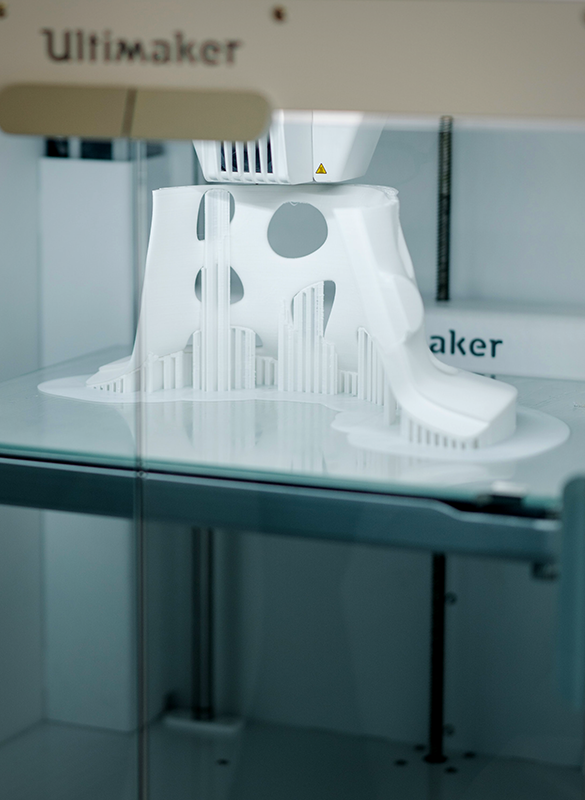


Why Use 3D Printing?
3D printing has a few advantages over traditional manufacturing methods.
First, it is much more affordable to set up a 3D printer than it is to buy or lease traditional manufacturing equipment.
Second, 3D printers can be used to create objects that would be impossible to create using traditional manufacturing methods.
Third, 3D printers are very versatile and can be used to create objects in a wide range of materials and mechanical properties.
Fourth, 3D printing allows for rapid prototyping or creating small batches of products, although it's not quite at the level of high volume production yet.
Finally, 3D printing can be used to create personalized products.
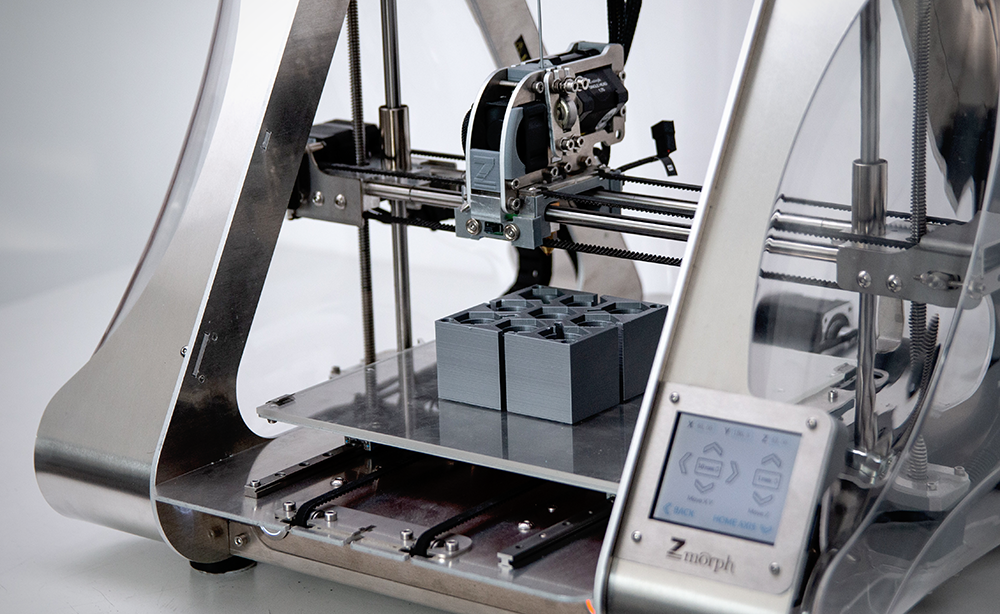
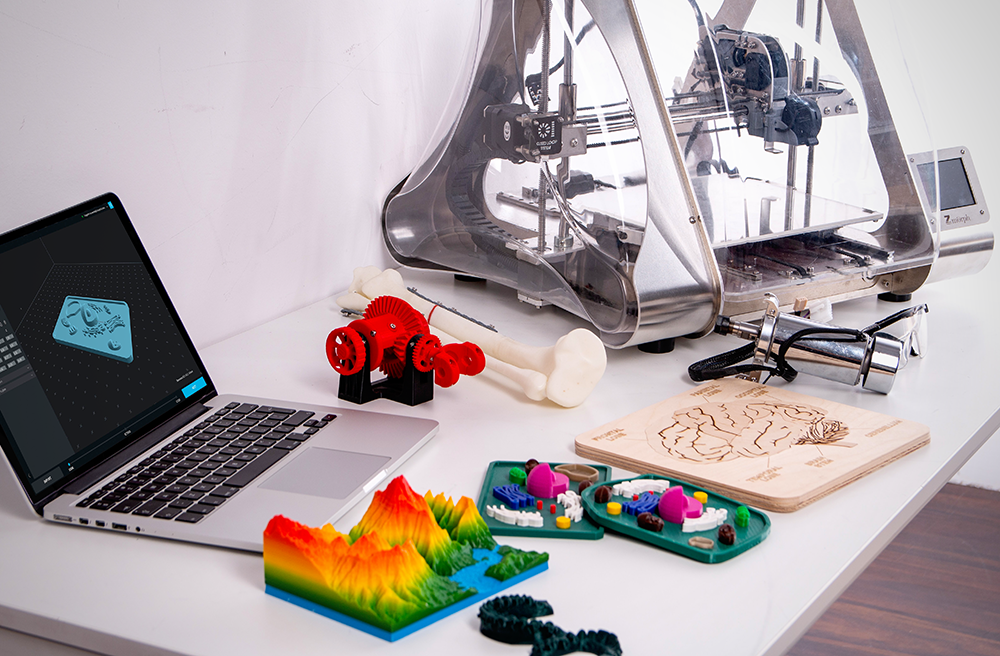


3D Printing for Art
Artists can use 3D printing to create just about anything they can imagine. Some artists use 3D printers to create small sculptures or figurines.
Others use them to create larger works of art, like statues or monuments. Still others use them to create functional objects, like vases, jewelry, or even furniture.
Artists can also use 3D printing to create prototypes of their work before mass-producing it.
3D printing can also be used to create limited edition prints of artwork.
And, finally, 3D printing can be used to create customized products such as phone cases or coffee mugs.
If you’re an artist who is interested in exploring 3D printing, there are a few things you need to know.
First, you need to find a 3D printer that is suitable for your needs.
Second, you need to find a material that you want to print with.
And third, you need to find a design software that you’re comfortable using.
Once you have all of these things, you’re ready to start creating your own 3D printed art.



Creating 3D Printed Art
Overall, 3D printing technology has come a long way in a relatively short space of time and its applications are growing every day.
For artists, hobbyists and designers, owning a printer opens up a whole new world of possibilities for creating fun projects at home.
3D printing is a great tool for creators who want to add another dimension to their work.
It is more affordable and versatile than traditional manufacturing methods, and it allows you to create objects that would be impossible to create using those methods.
If you’re thinking about using 3D printing in your artwork, the sky is the limit!


Interested in learning more about 3D printing? Check out Austen Hartley's video!
Want to learn more about different types of art?
Check out some of our art guides:










